TRACO 2017: Epigenetics and Case reports
Our first, speaker today is, Mukesh. Verma, I've. Known him for almost 30 years. He, and I both used to work at George Washington, University. And. Then. He came to the division. Of cancer prevention and. Subsequently. He joined, DCPS. In. 2004. As a program, director, and. He. Became the acting, chief of the analytic. Epidemiology. Research branch. And then. In 2007. He became branch chief of, the. Methods, and technologies, branch and so. He's going to talk to us today about epigenetics. It's not just gene mutations. Gene. Silencing is, very important, to. Thank. Study so. Today, I will, be talking about epigenetics. This, is a different. Way of gene, regulation, so. Since, I am from the epidemiology. And genomics, Research Program so. I will cover how. This, area is important, and how we can utilize that to. Identify people. Who are, at high. Risk of developing, cancer, as. Well as how a P genetic approaches, can be used in clinic, few. Of the drugs have been approved by, FDA, and what. Clinical, trials are being done and what, is the mechanism behind epigenetics. How gene regulation occurs so all those things I am, going to cover in the. Talk. So. Since I am from cancer institute, and we. Work on epidemiology. And genomics. Can. You hear well all okay, so. Cancer. As you know this is a serious. Disease in which prostate. Cancer and breast cancer in men and women. They are the number one killers and, 1.6. Million men and 2.2, million just with these cancers, they are affected, and this. Number is growing although. We have succeeded. Little. Bit in by. Screening. And other method, their survival. And quality, of life is better. In. 2010. It was estimated that, thirteen, point six million cancer survivors will, be there but in. 2022. We expect the, number will increase to 18. Million and, here distribution, of incidents, like new cases and how, much they survive in men and women they are shown, for different, especially. For colon, cancer or, breast cancer, screening, have been very useful as, well as early, detection markers. Have been useful in different cancers. Cancer. Is such a disease, that four major cancers, like. Breast cervix. Colon prostate lung, it, takes many years to develop and, those. Stages, which, come at. Different, times, those are defined, there so, our idea is that if we can characterize or, focus, more on early, stages then. We have more option. Options. For doing, chemo prevention or, therapy. Or other aspects, we can do. Initially. When biology, was developed and genetics. Was developed first, so. In that. Some. Mutations, in a specific genes and this is a model of colon cancer those, were identified, some, were for initiation, some, were for pre malignant stages. And then for invasive and those. Kinds of add more information were, useful, and based, on that and based on the age, and other time different. Terminology. Also you will see for. Breast cancer atypical. Hyperplasia, di c and all that and for, colon cancer also, so, that in genetic, terms and in, histological. Terms cancer. Was characterized, very much, then. Came the technology. When sequencing, was more popular it, was called a snip characterization. And then genome-wide. Association. Studies, what, happens that those are small changes in DNA. Sequence, whether, we can link to. The chromosomal, location, or not so, in 2005. Basically, first jiva's was done and these, are different, chromosomes. And as time passes by four, different chromosomes. Different genes were localized, which were associated. With not only cancer with others also so. By by, the time 2008, or 9 for most of the. Chromosome. Location, by, jiva's, they were identified. So. This is the situation now. Because, of that we wanted to utilize that. Whatever information in, genetics, is there how we can use. That for epigenetics. So. If you see in genetics, the way they have identified, four different kinds of cancers, and different. In our typical locations, how, many are they are where they are similar. Thing we want to do in, epigenetics. In. Cancer, model, basically, twelve. Pathways, which were Gerstein proposed there are the major pathways, so that has also, been characterized. Now. Comes epigenetics. So. In genetics, you know those are headed little, genome. Sequences, changes, or deletion, or addition, but. If without changing, the gene structure, gene. Expression, changes that is called epigenetics. So, we know about genetic, code and in, epigenetics we have to quartz methylation, code and histone code and, I will be discussing more about those, so. In your mind you can think, genetics. Will tell what, you are capable of, but. Epigenetics, will control when. Something, you should be done and doing and when, you should stop that so that kind of regulation is called epigenetics.
And By, terminology. Also epi. Means above genetics, so what is above genetics. Time. To time you will see in popular magazine some articles, that your DNA is not your destiny because, it was found that by, changing, behavior, lifestyle, and other things you can change expression. Of genes and in. Terms either you, can reduce their disease or just avoid, that and, to, distinguish, genetics, and epigenetics some. Experiments, were done in monozygotic, twins, where. Genetic, makeup was exactly, the same but, in that what was found that lot of discordance, was there either. In cardiovascular. Diseases, or other diseases, and that's, how, epigenetics. Came, and in that they found that without, DNA. Structure, change some changes were there and that gave us the idea of a B generate, predisposition. Like, if you see some epigenetic, changes that, person is at high risk or. The way pharmacogenomics. Is like based on genetic, background people can treat. Same. Way. Epigenetic. Background, also that. Is giving. Rise to pharmaco. Epigenomics. Or personalized. Medicine. And. This. Year also analytical, came that cancer epigenetics, at their driving seat because now such. Changes, people are identifying, which, are the starter, point when. At a stem stage you are there there are no mutations you snips are in, Dell or any kind of changes. But. Gradually. Methylation. Changes or, other changes. Epigenetic, changes they arise to. Give you a little bit background about chromatin, it, is made up of histones, h2a. H2b h3, h4. H1. Is just a linker and these, are 146, bit base pair long and, they, are a test to neutralize, the charge of. DNA, and to stabilize, chromatin. In. Promoter, region, CG. CG sequences. Are very, common. Normally. This cytosine, is there but sometimes, especially in, disease initiation. Cytosine. Gets methylated, at. Five prime site and that. Can cause gene. Suppression. And. It is observed, in tumor suppressor, gene at, the same time some genes are such where promoter, CG. Sequences. Are already, methylated, and they get hyper methylated, and that, was observed in oncogenes. So, four different genes different, kind of regulation, is there in. Epigenetic. Regulation, mostly. Components. Are either methylation. Which is. Done by DNA, methylation methyl, transferase, genes number. One three a/b difference, are there some. Are for initiation methylation. Some are for maintenance. Histones. Are there, which. Get. Modified either by acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation. Or other kind, then, comes a non-coding RNA, like micro, RNA and others they, also regulate, gene, expression. You. Will hear few terms also recently were introduced, like shores and shells like. Those see CG, sequences, if, in 0.4, KB region 60%, CG sequences, are there they, are called CPG, Island, but. If those sequences. Cpg, sequences are, less. Than 2 KB then. These are called shores and 2 to 4 KB they are called shells and other, area is called open, sea so these are that terminology, time, to time they are coming. So. Regarding, component, of epigenomics, as I mentioned methylation, regulation, is the main one done. By methyl, transferase, genes then. Comes histone modifications. Compact. My compact, chromatin, vs relaxed. Chromatin, that is done by different modifications. Acetylation. By generation, methylation. Phosphorylation. Ubiquitination, in, between comes micro, RNA as well and some. Non-histone. Proteins like, polycomb, group of proteins or. Chromatin. Folding, proteins they are there for, histones. Different, kinds of enzymes or proteins are, there, that. Has been characterized, now, some sequences, are called repeat sequence, a loose sequence zero sign and line they. Are very much involved. In genomic, instability so. They are important, from that point, of view, genome. And epigenome, when we characterize, genome. Since in all cells, the same kind of DNA is there where that you take from blood or lung or colon you. Have to sequence only once but. Epigenome, is dynamics, so anytime you are doing longitudinally. Many samples you have to take that, changes, and they work, in. Coordination. And. In monozygotic twins, many studies, on different diseases. Have been done in, some diseases like neurological. Disorders, another genetic, component, dominate, while, in cancer, and few other diseases, epigenetic.
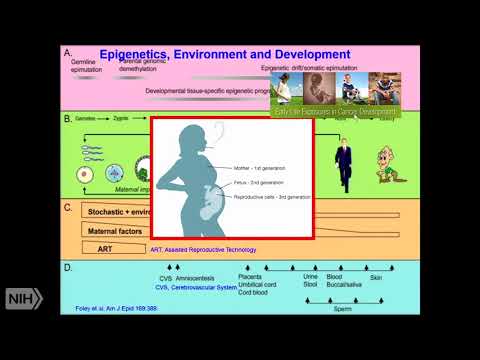
Influence, Is more and they, like genetics, by, diet. Or lifestyle, or, environment. Epigenetic. Changes happen now. More important, is that when. Epigenetic. Error can happen so usually the. Order, of error which can happen that is quite early before birth or after birth you can see based on the weight. Or how, many order, of. Defects. Can happen early and later, on they, are less, and, in, this figure if you see, that. Mostly at initial stages maternal, factors or, environmental. Factors those together influence. For. Initiation, of disease later, on it becomes mostly, lifestyle, in tight so, that's how they have defined and at, the same time at different stages, of life cycle, different. Kind of biospecimen. Or samples can be collected which, can be characterized, for. Epigenetics. If. You think about some pregnant, women then. If that. Person is smoking, then mothers a generation, that is affected, then fetus and then, reproductive, cells so even three generations. Can be affected and. Epigenetic. Changes are more susceptible, than, genetic. Changes. So. At NIH, as, such, or at NCI we emphasize. On early, life exposure, how we can utilize that and. Another. Point I want to mention about risk, assessment or, identifying. High risk population. If you want to do that then few things are essential, like we. Want to have certain, populations. Where disease, have not developed but, you have all information. About exposure, whether chemical radiation, infectious, agent toxic substance, family. History diet medication. And these. Biospecimen. Should be collected, non-invasively. Then. We need follow-up like several times you have to take, what. Are the challenges are drawbacks, in these kinds of experiments. Or the study design that these are expensive. And data-sharing. Many times people don't do but they should do but, advantages, that these are essential, if we want to identify yuka these are the factors. Contributing to your disease so, that you can develop some Terra. Boutique approaches. So. In our program, we. Have samples. From different population, whether african-american. Asian. Latin, American, or Hawaiian. The, reason is whenever a drug is developed all people, for of different, racial and ethnic group they don't respond, the same way so, we want to get. Involved. With other populations, also so, these are the countries from which we, collect samples we support them and they store, that and we have 2.3, million. Subjects. Are there a specimen. And those. Cohorts where disease have not developed but we have access to those several. Of that our program, supports, and some have been going on since early, seventies, like. Nurses healthy studies or physicians. Healthy studies so total sixty four cohorts, our program, support, and, membership, should be that minimum 10,000, samples they should supply and that. Way we get those. Jiva the studies, were done and then the same sample or same people we are using in. Future to collect samples. So that by epigenetics. We can analyze so. Time to time to promote this program we write in different articles. Different, journals, articles like, early. Life exposure, to infectious agents, and later cancer development, that I did, before some time and. At NIH, level some. Money is congressionally. Mandated they. Say that you have to spend on certain area, so.
This Program one and half year we initiated, is called, eco or environment. And influences, on child health outcome. There. Before, pregnancy, those. Mothers, are enrolled, and some are already having, small children or. Babies, so. In that. About. 165. Million dollar per year will be spent. And for seven years it is committed, and then. In this program, we have data analysis Center or death. Center which can do. The actual analysis, or genetic, code or Coordination. Center so that's how it is done and. Different. Life stages, are there where samples will be collected like, preconception. Anything. Prior to Labor perinatal. Infancy, early, childhood middle. Adolescence. And this, for seven years that will be followed and chance, is out that for next seven years also it will be followed so when. Early. In life you get exposed, and which disease you develop that will find out and once you find out then, you can go back to those samples, to see whether, any molecular changes, you can see which, you can correlate with Europe with the disease. Epigenetics. Has been associated with behavior, also and some. Papers you will see like epi. Genome wide Association, studies, which correlate. With aggressive, behavior many. Things with genetics, we could not understand. Which with epigenetics. We can do this, was for biopsychosocial, pathways. In, epigenetic. Regulation. And. Many. Times we hear about health disparities, which. Is in socially. Social. Economic, background. Those, people who do not have good. Resources in those disease were developing, so in that also what we are proposing that epigenomic. Profiling, they should do so that end of program also we, are promoting, and. In. This we. Have shown like genome-wide Association, studies, you do similarly, those, components, like methylation, profiling, histone. Profiling, or micro. RNA profiling, or chromatin, competition. Or chromatin, accessibility that. You do but if you put this together then. You can get, better results and better sensitivity. To those biomarkers, and. Epigenetics. Also is affected by radiation infectious. Agent toxic substances, that such are and ultimately that. Intermediate, phenotype, comes and this, is develop in. This also we face some challenges but, we have proposed, also certain, kind of solutions. For example sample, collection what kind of sample should be there what, a study design, is there what, technology. We have whether high throughput is there or not and I am going to tell you also about the. Technology, how these epigenetics. Is done. And in. Environment. Those. Agents, which previously used, to be. For mutation. Only now arsenic. Benzene, cadmium, chromium, Nicoll and all, these have been found that they do epigenetic. Changes in different kind of cancers, so, that way more, and more evidences. Are coming and. One. Paper came about, cross-generational. Effect, of alcohol, dependence in. That also methylation. Was, the regulatory. Mechanism. The. Way toxic. Oh genomics, is there by dodging, some genomic changes are there now people are studying that before, genomics.
Epigenomics. Also are, changing, so those are called toxic, Oh epigenomics. Changes, and this. Slide I put that whenever. Some abnormal. Thing happens whether exposure, or infection, other things then, fasting affected will be transcription, factors, or cell, cycle regulators, in, minutes. To hours that can happen if. Those expose. Yourself for a little longer like eight, hours or one overnight. Then methylation, changes and/or epigenetic, changes you can see and, here, I have not shown but in 24, hours or two days you will see metabolomics. Changes, but, it is for very long time then only genetic changes can come that. Also emphasizes, that if we can detect those changes early then. We can do. Something about the. Disease, and. Here we have shown like in different cancers, the way about. Genetic, information we, know similarly, now about. Epigenetic. Epigenetics. That information. Is coming and in fact certain genes, have been identified which. Regulate. Methylation, but in that methylation, these mutations. Have been reported, so, they are, going, in some cases both, ways. Peter. Jones and Andrew Feinberg Peter, Jones is at Michigan. And Andrew Feinberg and Johns Hopkins they were the pioneer, who started, thinking about epigenetic. Regulation in. Which they saw that when active. Transcription, is there then. Histone. Is acetylated. At, inactivation, it starts, getting deacetylation, and at complete silencing, it gets methylated by DNA. Methyl it turns transferees, and if, you see chromatin. At top then chromatin, is it, is called relaxed, or quite apart, and yellow, color shows, situation, but, gradually, this red-colored methylation, starts, and many, other transcription, factors, other gene regulatory, factors, come and these. Chromatin, get so compacted, that transcription. Stops, and there's how epigenetic. Regulation, works. And. When. Methylation. Is also done then one strand is methylated at one time another at other, time and SLT. News in methane and that is converted, to SLE. Nurse'll homocysteine, so. Whenever you do such kind of experiments, both strength, should be sequenced. At. Different. Stages. Of cancer, development these are the mutations but in epigenetic. Changes, overall. Initially. Because. Of line and sign sequences, which cover about 90 percent of the genome they are already, methylated. Their CPG, sequence so, gradually, with disease development, or lifelong global. Hypo methylation you, will see but, for a specific, gene promoter gets hyper methylated, and histone, modification, initially, they are not there but they increase, in cancer. So. This is one paper where they have measured that Lineman, methylation, status in, prostate, cancer how, it increases, so, very systematically. That was done to, show line one these, are also called jumping, genes so, initially they just knew that they will go somewhere but because, of epigenetic, regulation this. Happens. Methylation. Also, can, happen in three ways either, abnormal. Increase or, decrease, or no change in, increase. Like. In tumor suppressor, genes either. Methylation. Of both alleles or one allele and imprint. DNA. Imprinting, of one gene and other is methylated, in abnormal. Decrease, it. Happens in proto oncogenes or. Latent. Viral activation, if. You remember in early 90s, when. Gene therapy just came then, retroviral, vectors. Were used to introduce healthy. Gene into the other by recombinant, technology. Since. Retroviruses. Were used so many times they are promoted, which is called LTR. So, those got. Hypermethylated. And inactivity that's why those Vector did not work and recombinant, DNA also did not work but at the time methylation, are the things were not very, well characterized, now we know that so now such vectors are created, with where, that problem does not come, there.
Are No changes there then either chemically. Induced mutations, or. Pure repair, or deamination, so these are different, combinations. Or. Possibilities. Which can arise due to DNA, methylation. Here. After. More, results, at different genes have been identified which. Are involved, in epigenetic, regulation but some genetic, changes have also been reported. Although. This question comes whether genetics, came first, or epigenetics, came first but, when. Whole. Epigenome. Roadmap, initiative. Was. Started and, in, normal. Cells, epigenetic. Profiling wisdom then it was found that epigenetic. Changes came, first but now we want to know how they are correlated. Even. In different, and network or pathway different, genes of pathway have been characterized, in terms of what. Kind of epigenetic, changes are there here, I have shown integrins. Signaling. Now. Ten years ago we did not know about micro, RNA, much they were in drosophila, plant but, then they were reported, in animals or human and now, we know that even cancer is specific, micro. RNAs are there these, are 2225 nucleotides. A small RNA. Molecules, which, are very stable and because, of their secondary, structure, and they, can be used in epidemiology. Or epigenetics. By, two ways either you do micro, RNA profiling, and you know which group, of micro RNA are increasing, or decreasing based, on that you, can tell whether some, diseases or, cancer is developing, or not or response to therapy all those, genes which are coding for micro RNA if there is any polymorphism. That also you can follow. Micro. RNA they either, increase. Or decrease so, for different. Diseases that, people, have followed so, for lung cancer micro. Rna's, be different than liver cancer, and nowadays, another concept, is also coming about exosomes. So. Somehow among, all RN. Is micro, RNA are the one which gets concentrated in exomes so, those from, that can be collected first of all non invasively, and, micro RNA from that can be characterized, and can use for clinical, purposes, so. This is the one we, wrote before some time extracellular. Recycles, or exosome, and how, we can utilize that so, lot of research is going on and those. Extra somes contain, not not only micro RNA some time DNA is also there or protein or metabolite. So, how they can be utilized. Regarding. Histone as I mentioned, four kinds of subunits, are there and these. Are the tails of these histones, which are, modified, whether, at lysine, or other portion, and these, modifications. Are. Shown which, in different cancers, those have been reported. When. We initiated roadmap. Epigenomics program. At, nih then, what we did we gave contract, to two companies to, raise monoclonal, antibodies. Against these modified. Moieties, these so, that that can be used for, screening, purposes and, that, was distributed to different investigators. And. They. In. Those histone, modifications. Some. Will be for, writing, the instructions some will be for removing, so, all those also have been characterized, and along. With histone, other proteins, are also being characterized, and now technology, exists like it is called chip on chip so. By immunoprecipitation, and, other techniques, you can identify. First. By breaking. Chromatin, and then precipitation. That, which chromatin, or modifications. Are there and at, different times you can identify and. Sequence. In which sequence which histone. Modifications. Are important, and cancer. Related histone, modifications. Most of them are only 9, to 11 so. If anybody starts any project, for screening, purposes or, other purposes, then, we recommend that those should be used, and here, they are shown like s3 protein at lysine, for a lysine. 9 or, 27, where, this is their and where they are acting whether they are how, they are modified, so all those have been characterized. And. These. Are used for diagnostic, purposes, also. Histone. Modifications. And to combine and promote the field time to time I have edited, different books either on a cancer epigenetics. Or cancer, epidemiology. For who susceptibility. Factors or, modifiable. Factors or, cancer biomarkers, but this year was on, progresses. And challenges, in precision medicine as. You know that every individual is different so, how we can utilize this information, if the doctor follows a patient, and, take. Samples again, and again I was. Interviewed, one time by nature to know why. Epigenetics. Is important, compared to genetics, so, then I emphasize, that if. You have mutation, or certain changes in gene you cannot go back just you can use that to, tell what, disease will develop what can happen but. These epigenetic, changes methylation, and histone you, can reverse so. Epigenetics. Has slight edge over genetics. And. Then. Next year again I was interviewed, by the same Journal then by. That time certain. Drugs. Were, introduced. Or identified. Whether. They were demethylated. Or histone. Modified, but if they can do histone modifications, so those were also identified in, different, pharmaceutical, companies, they, started, working on those drugs we call those epigenetic.
Inhibitors. In. Methylation, projects. Different, kinds, you have to keep in mind as to keep different. Kind of control to reduce false. Negative, or false positive, like, total methylation, content, or material. Level at a specific stage, or pattern. Or profile, of methylation, of either specific, genes or a number of genes or pattern. In whole epigenome, but. If all these controls, are properly, maintained, then, methylation, profiling, will be very, accurate. Stable. In who is also in johns-hopkins, Hever works. On clinical, epigenomics. Or translational. Epigenomics. Mode and they. Have characterized, more non-histone, proteins as, well as diff and transcription. Factors and other factors, and histone their, sequence, when they combine and when they are released and they. Do that kind of work suppose, in. H3. Histone, K 27, is tri methylated, then, the gene will be involved in differentiation or, if. Next. Time you know acid in this case s 3 K 9 methylation is, serine then. Change, will be permanent, so those kinds of basic research is also going on. Now. I different. Stages, of development of, cancer like progression. Early detection then, diagnosis, or therapeutic time. In. These stages. They. Different. Exfoliated, cells come so, if these samples are collected, then. Many markers, can be characterized, from that. For. Different types of cancers, after doing. In. Investigators. Have done in different setup, or Institute group. Of genes have been identified which. In these cancers, will be hyper, methylated. Similarly. Other. Kinds, of proteins. Are there, in which methylation. Changes or, other changes are there those. Also have been characterized. Very well. Against. Those proteins. Or methylation. Changes in. Different, drugs, are being developed these are the ones for methylation. Changes in, differential, trials or histone changes, in, that some of the promising, results, are also coming although. Sometimes some adverse reaction like dehydration. Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Those you see but. Still against, had, histone. Acetyl, transferase, or d NM T's against, that these are those, drugs which are in pipeline, whether, is it is Johnson & Johnson's, or the SmithKline Beecham or. AstraZeneca. All of them have programs, against. These epigenetic, drugs. If, you get, a chance to go to s Co American, Society, of Clinical Oncology, so, latest results, are presented there and. These. Inhibitors, belong to different classes, short, chain fatty acids or aliphatic, compounds, or cyclic. Fights but, benzoate, and same. Way histone. Deacetylases. Are also being, characterized, like different, forms are therefore against different forms, also those. Inhibitors are being developed so these, inhibitors. Provide, a noble, class of anti-cancer, drugs and sometimes, they work as radio sensitizers. Like, regular. Treatment. Treating. Agents if you put and many patients, will not respond, but if we treat with epigenetic, inhibitor, first and then you use the regular drug then it starts, working, an. Example. One, of this is there where, as I cited in for. Methylation, drug or valproic. Acid histone. Drug that was used in, those patients more, than 50 where no other drug was working so. This combination was, giving and by pyrosequencing. This, methylation, was done and chip and chip analysis, a stone was done on day one ten and twenty eight and they, started, responding. Similarly. In other example. Combination. Of five azacytidine, for, demethylation, valproic. Acid or, all-trans-retinoic, acid, for. Myeloid, leukemia, and miler, dysplastic, syndrome, that was used, whenever. That responds with other drugs was not there but then they observe that these drugs, can improve. The. Cancer. Development, and. At. NCI, we have several, clinical. Trials are going on here I have shown for histone, inhibitors, whether, these are solid tumors, or leukemia, or lymphoma breast, cancer, glioblastoma. These. Are different trials. In which these, epigenetic. Inhibitors. Are being tried similarly. For methylation, inhibitors also. On solid, tumors on or. Leukemia. Or myeloid, leukemia, or prostate cancer these are being tried and. That, I already mentioned the schering-plough Bristol, Mars all, these companies have many. Of. These inhibitors, in their pipeline and the, idea is the same like this both inhibitors, should be tried either alone, or in. Combination, only. Anyway epigenetic. Limiters or with other inhibitors, and several. Studies, show that those. Promising. Gradually. FDA. Also found. Those studies, useful and for epigenetic. Inhibitors, so - for methylation. - for histones, those who are approved by FDA later. On now, we have altogether one two three four five six six, inhibitors, are there which are FDA.
Approved So, it is not just like theoretically. Epigenetics. We are understanding, but, that is in, clinic, also and, Nature. Reviews put, something, about clinical trials we are epigenetic. Therapy is, going on so, that you can search on your own if you are interested and there, you, will find that information was, what was the combination, which was given first how much was the dose what. Kind of background, of patient. Was there all those kinds. Of information. Is there and time, to time we also write about how. They are doing in different kind of cancer in, those studies which we support, from other program, like, this is combination, therapy, of epigenetics. For lung. Cancer this, one was for him ultimate, illogical, epithelial. Tumor cells. So. Now I will tell different, kind of cancers, where epigenetics. Has been studied, more this. Is for colorectal. Cancer. In, which methylation. Changes in whatever genes they are there they are shown some, are at very early stages some are at later stages, but. Along, with genetic, changes and epigenetic. Changes we follow. Microsatellite. Instability, also, and in, fact in colon cancer. CPG. Island methylated. Phenotype, or sometime people called it simple. Phenotype, that was observed what, happens that left side of colon behaves differently than, right side of colon. With. Respect, to EGFR, receptor or, B rff mutation, or. This. MSI. Microsatellite. Instability high. Or low or methylation. Pattern these, sites are different, and they respond, also, differently. To different inhibitors so. In that only, by epigenetic. Characterization. It was found that colon cancer should be treated differently now. Another area is so coming off microbiome. Where. Microbes. Or. Microbiota. They make their colonies, in colon, and they. Make biofilm, so we want to integrate that data with this and see whether that can improve, our treatment, or not but. Just by methylation, profiling, when, that was done then. Kara's, mutation, or BRF a mutation and reference I high or dis methylation, they, came in a group and we could, identify a, group of genes which. They are used along, with MSI, they. Can, tell. Who is at high, risk of developing colorectal cancer. So, it is not like a screening. Only, you have to do but, other some non invasive technology, also, you can do for detecting. Colorectal cancer. In. AML. And ll, acute, myeloid leukemia or, lymphoma lastic based. On methylation, patterns, healthy. People could be distinguished, from a ll or AML, in. Case of lung cancer, along, with proteomic, marker, these, epigenetic. Markers were used and even in East put'em you can do that test and history, balance ki has done, this kind of work. Asbestos. Exposure in, miss totally, Mia just. By methylation, profiling, those two groups can be identified, and these have been done a large number of people. In. Each of AGL cancer Barrett, is the early. Stage, so. Methylation. Pattern in 20, genes or so if you follow that. Some genes are methylated, at early stages some are that later stages, so, longitudinally. If you follow the same patient, you can tell that that person. Is at high risk of developing this. Cancer, and that. Methylation. Profiling, can, be correlated. To, survival. Also after. Treatment, whether patient, is surviving, or not, many. Times people ask that for cohort or clinical, trials why we collect information regarding. Patients. History exposure, history or others but, it is very important, because, if somebody is alcoholic. They have Kara's mutation, long-standing. Diabetes and, for, pancreatic cancer currently. We don't have early detection marker. But along with those features 5016 and p14, they, get hypermethylated. Then it means those, people are at high risk of developing pancreatic, cancer. Otherwise. Pancreatic. Cancer and ovarian, cancer, are such that. In one or two years by the time it is detected it is too late for, breast. Cancer lung, cancer colon, cancer and. Some. Other cancers, it takes 15 20 years but these are such very fatal. Cancers. In. Breast cancer, treatment. Can also be followed by based on methylation. Profiling. Now. Comes those infectious, agents, many infectious, agents, like HPV, sv40.
@cv. EBV pylori, they, have been associated with many other, cancers in fact if, we, see all cancers. Then in 15%. Of total cancers, infectious. Agents, are involved, and in, that latency, associated nuclear. Antigen, or epstein-barr. Virus nuclear. Antigen, they are the main. Genes. Which are involved. Recently. For papilloma, virus which is for cervical cancer or EBV, for ezel news. Of pharyngeal carcinoma, or for liver cancer whole. Methylation. Profiling has been done why. We are interested in these kinds of research that just, by. Pathological. Examination or histology you cannot tell that a person, will develop those. Cancers, or not but, if we know these profiling, then we are we. We know that the person is at high risk. So. Here. Like, in HPV. Early. Genes or ECC 7 or late genes are there whatever. Genes when it is methylated, and what was the extent of methylation, at different stages those. Have been characterized, completely. And. To. Promote this area we have put on hiv/aids. Or other viral. Methylation, also that area we are promoting, or. For. Liver. Cancer in that hepatitis. B or C those. Are being characterized, and in, hepatocellular, carcinoma. As you know mostly in Asian. And Japanese population. Is there so one, gene was observed. Hypermethylation. Was observed, only in Japanese population. So, sometimes, some changes are very, much population-based some. Are very. Common, like, for hepatocellular, carcinoma. This. Group of genes generally. Gets hyper, methylated, in. Immune, system also T cell or b-cell during their development or doing, their different, functions. Epigenetics. Has been characterized, very, well. And. T-cell, methyltransferase, in cancer. And other diseases those, have also been characterized. Now. In prostate, cancer mostly. PSA. Is the one which was you are is still being used but, when level is less than full mana gram per ml then, clean, GL does not know whether they should wait or they should treat because. Prostate, cancer as such it takes a long time so whether go, for surgery or chemotherapy or, radiation but. Then GST, p1 methylation, came in, such a way that in most of the cases those. Hypermethylated. Groups, that they indicate. Better. Results, and then comparison, with prostate. Cancer results, udom then. Epigenomics. One company, was, there which developed, this test and they worked with quest Diagnostics. And now, that quest, diagnostic. They do for, prostate cancer death test also and they have different prices, in. Bladder. Cancer. Exfoliate. Exfoliated. Cells which come in urine, if you collect that those have, sufficient, amount of DNA which you can use for methylation, profiling. So, bladder cancer, like lung cancer and bladder cancer with smoke, or tobacco they are affected, so that you can use.
Now. That also happens about methylation, profiling like Peter. Laird in University of Southern California, with. That many. Times what happens that cancer at one, stage it is in one organ site in another stage. It is on other site or, sometimes, secondary cancer also comes so, he uses the pattern and can identify which. Other cancers, a. Person. Is likely, to develop or prediction, model so they develop based on that. Now. Comes a little bit about prevention. As. I mentioned, that epigenetic. Changes, those, you can. Reverse. So. In that it is our understanding that cancer, since most, of the time, environment. And lifestyle, and diet and exposure, day play major role so, if you change that then you. Can prevent cancer in, fact 30 to 40 percent cancers, are preventable. So. That kind of research was done and in liver cancer one model was developed we, are no carcinogen. Was added just methyl, donor was. Supplied. And such kind of situation, was developed, it was very similar to liver cancer and then. In different, food and their. Biological, components, those were characterized, for, example, in turmeric cinnamon or apple, or citrus, or coffee broccoli, garlic etc so. Some food have D. Methylating properties, some. Have only histone. Modification. And histone, modification. Properties, some have both so. We have Institute. Of alternative, medicine where they are trying. To utilize that nature or food how they can do and how much epigenetic. Mechanism. Is going on I, also. Wrote one article on, nutrition, epigenetics. To, cover that area, now. Comes of what NIH, has done to, promote this area. When. Dr., Zerhouni was director, of NIH that, time he initiated one program, that about, 1.5. 1.2. To 1.5, percent, of budget if all, Institute contribute, then. That, can be utilized to understand, such. Biology. Which individual, Institute cannot support, but, it will be very helpful so, in first round microbiome, and epigenetics, these two. Programs was, promoted, because epigenetics, that, in several, disorder. That was observed, but, it was not known the way we have in genome from, healthy people also we have sequence, in proteomics, we, have proteomic. Profiling, but, for methylation, profiling, and histone and micro, RNA and others we did not have so, this epigenomic. Roadmap, program, was initiated. Idea. Was of that roadmap program, that for, five to ten major, project, can be started which are of high risk but, for. That. They. Can contribute a lot in translation. Or transformative.
Biology. So. After, that other. Directors came and the. French is calling came so he changed its name to Common Fund and as. An, example you can see that, in. 2015. And 16 also, almost the same among about, half billion dollar were. Spent. And I, have been involved in three, major programs, from the start, epigenomics. Roadmap, program and then. Metabolomics, and then. This. Molecular transducers. Of physical activities. So. In that. We. Are doing such a research which is for healthy, people what kind of profiling, is there or increasing. The capacity to, do that kind of analysis, so that is done and these are other programs, which are going on like, single-cell. Analysis, there are global health science. And behavior. Genomic. Humour expression. Etc, so. For epigenomic. Roadmap you can imagine and these are all, congressionally. Mandated programs. So first money will go to this program then only it will be distributed to others so. In 2008, we started and, we, did. It that for, mapping of different. Sites. For epigenetics. And let. Me show you this light and nature covered the two years ago whole, epigenomic. Roadmap what kind of data we got so. Since, for. Different, organs, different, tissues, have different epigenomic, profiling, so, about, 112. Kind of cells were characterized, from brain breast, liver duodenum, so these are the size from which cells were collected, protocols. Or essay standards, were developed and then. Complete. Epigenomic. Database, was created and complete, means like methylation. Profiling histone, profiling, micro RNA and DNA is. One mapping, so. These are the types of cells shown here which were taken and some, from stem cells also so, now we have some reference. So, that we can use that if someone develops a disease that what kind of changes are in healthy people what, kind are in, the disease, person and. Through. That several. High. Quality, papers, were also published during. That time. On. Parallel. Internationally. Also several a first were conducted, and one of the example, is international. Human epigenome consortium. Or. I hack this, in Europe it was developed. And we. Participate. In that so, that there is no overlap they, want to do in model organism, also and other, disease also they want to develop, and their idea was that about. A thousand, epigenome, they will be doing so. When, we had our first meeting that. Time these are the countries who, participated. In that and then. Funding, agencies, were also different like we are funding epigenome. Roadmap but other people, came and. Industries. They supplied. Mostly, equipment, and other resources, and, nature and science covered. That and every. Year i hack has annual meeting where we update, each other and you, see our american association of cancer research they. Also cover that this, is I hat website, so they keep, track of whatever. Is happening in Europe Asia and other places we keep track of us but, we, exchange. Our views and conference, calls at, least twice, in a year. Now. Other, challenges. Which are coming to bring it to clinic, how at NIH, or NCI we are doing so, we usually write, articles.
In Which we write these are the future. Research program, where people should do research so this we did on epidemiology. What are the trends and challenges or. Molecular. Profiling, how we can use that for personalized, medicine or precision medicine, and. Then. Why. I initiated, this program, this. Was called precision, medicine initiative. So. In that idea was that about thousand, 1. Million people will be enrolled and their. Electronic. Records. Will be maintained, for them from the start and whenever tree when tis there and when they. Are, undergoing some kind of analysis, and their, data will be available, to all so. This was. Initiated. And then recently. It's a name was changed just, all of us but program is the same but, this is also done by congressionally. Mandated, program. Since. Those kinds of information are, coming like one. Driver one si will not work for all and more. More, and more whenever. You go to a doctor, they, record, electronically. Your information. And whatever, is not, recorded. At all so we ask them to put that for future so. In these these will be very useful in, future although, as it, happens here also we have by. Informatics. Challenges, or recruitment and others but, we think that we are in right direction, then. Came 21st, century, curette, in which moon short program came from NCI, and, NHGRI. That. Genome Research Institute also. Participated. In this, program these two institutes were giving additional money, about 350. Million dollars and, this is also for many. Years here. Idea was that whatever research is going on in translational. Epigenetics. Or other kind. Of program. Then, how. They can make the, speed, faster, how you can bring that quicker. To the clinic, so that has been going on now, we have written those programs, which are called funding. Approach it in opportunity. Announcement, or RF is and then, people are going to submit their project and by. Media, next year FY 18 we are going to fund this. Program and. To. Promote that personalized, medicine, other articles, also we write or in, Cancer Epidemiology because, this is the way to, identify. Different. Kinds of risk factors or causative, agent we promote, that epidemiology. A lot. By, writing these kinds of articles, or. Stem, cells how we can utilize that so. What are the current, research. Opportunities. And challenges based, on what I gave you background whether. These epigenetic markers. Or these profiling. They can help us in identifying new. Risk factors, or can, establish that what factors, we have those. Are good for different, races, and ethnic group. Then. Whether, case control studies, or cohort studies, or which, study, design we should follow to do that kind of research, how. Much correlation. Is there in genetics. And epigenetics, and, whether. Racial. Or ethnic is specific. Micro. RNA or long non-coding RNA. We can identify, or. How we can use these. Kinds, of information for. Different subcategories. Of, subtyping, of cancers, as, you know in breast cancer as such it is one breast cancer but eleven kinds of cells are in even, breast cancer so, that molecular, subtype see subtyping. Many times for. Those, pathologists, who are trained earlier it is very difficult for them to distinguish and, they, responds, to treatment differently. But by molecular. Characterization, that can be done. These. Are my. Collaborators. And I want to leave with this code, that our genome, and it's, super imperious, epigenome. Code this. Is the journey we have embarked on one. That is spared the roadblocks but, also with many amazing discoveries, and success stories both. In cancer, medicine and cancer, science we, are privileged, to be part of those and to, share them with all of you thank you I. Will. Take any questions, or clarification. Or I did, not cover well. In. Different cancers, that they are giving, different results. Sometimes. Histone, and sometime, methylation. But best, results, so far in clinical, trials are coming from those, where. Regular. Agents, they, are not that much effective, but, if you prick it with, histone and then. After, some time introduce, methylation. Inhibitors also, then they give good results so, it is a matter of which, we should start first which, and how, much it does we should use. But. Many more are coming and also. Especially. In his system D SAT list different, forms, have been identified, so.
Pharmaceutical. Companies for different, forms they are creating, those inhibitors, but. They are coming very well and now we have at least six such established, they, are being used and when. Thing as you know that with the time or with the age we, collect so, much somatic, mutations, and he sniffs and all those some, come with some, come with the disease but, we cannot go back but, if we can identify these, then, probably, since they are reversing, than it does, good but. It's still best way is that people. Change in lifestyle, and then use, those natural, food and other thing then you can prevent, and do, that because they have inherent. Epigenetic. Inhibiting, properties, many of those foods. That. Is very, well that, at least has come, out and that's the reason that one and a half year ago that echo program was initiated. Environment. Influences, on health, child. Health outcome, the. Reason were and, also to do that what, was the condition that, those. Centers, which want to do that research they, should have ongoing, studies, and they are enrolling, pregnant. Mothers or they have that so, eighty-four, cohorts, were identified, so and 34, investigators. We funded, so. They are doing their own research but, we have, come out with one common protocol, and common. Collection, of materials, like nail, hair, and. Psychosocial. Stress. Income. Education. All those data, is being collected and, whenever, they go to clinic, whatever biospecimen, they can do and molecular analysis can be done that is being done and those. Mainly those will be followed for a long time, otherwise. In disease. Diagnosis, and prognosis what, was happening there, when you are very sick then doctor is seeing you and then based on their they are prescribing, but. They did, not know when. It is started whether we can stop. That early, so. On early, expose our emphasis is very much so with, NIH s, National. Institute of Environmental Health Sciences and we worked, together. Alright. And. We have some announcements and. Our. Last class for this year will be next Monday December, 4th and we'll. Be having lectures on pancreatic. Cancer, in, nanotechnology. And. Unfortunately. I'll be out of town then, so dr., Zia who gave. The breast cancer lecture, she'll be here. Distributing. The handouts and introducing, the speakers. And. Then, when the class is over. It's. Possible, to get a certificate, of completion of the course and. So. What we'll be doing is, by, December, 11, we'll be posting the. Final. Exam, and. It's. A multiple guests exam graded, by the computer, it's got one question, from each of the lectures and, if. You get 70%, of the answers correct then you pass and. The. Exam will be online for about a month and. Then. Hopefully, at the end of January, we'll be printing the certificate, it's usually about 40, to 50 people from, Traco. Actually, complete, the course and get the certificate. So, if. You have any questions, on that contact, me in, our last lecture today is by dr. Ola Coe of, the division of cancer treatment, and diagnosis. And, for. Traco many, of you visited, the tumor boards, and heard. About. Case. Reports, and today dr., Ola Coe presents, the case reports, to you thank. You. Thank. You thank you for staying, behind I really appreciated gonna. Talk about case reports. So. The object. Is what I hope to achieve. During. This lecture is to describe. The history, of case reports.
Recognized. The, potential, rules, of case reports. Disk. Case, reports. Outline. Pertinent. Information, for. A good, case, report. Case. Report, is defined, at this, one definition, is a formal. Summary, of a. Unique patient and his. Or her illness. Including the presenting signs and symptoms. Diagnostic. Studies treatment, costs and outcome. Case. Reports probably started. The. Old X example, of probably the, preserved, medical, literature. Containing. Clinical cases, from. Egyptian. Antiquities papers. And that. Was, thought. To be around, 1600. BC, some. People felt think, that they were probably rewritten. Text, from some. Centuries, before that time. Among. This 148, cases discussing. Injuries, or disorders, of the head and upper torso. Case. Reports. Describe using. The. Centuries, in which they, were written or by, the. Main. Actors. Of. People. That were involved in in the writing of the case reports, so, for example, we have what's called the Hippocratic case reports, and this. Emphasize. Accurate. Descriptions, of only clinically, relevant, findings. And. Mostly. Physical Arment and physical and mental findings, were described, and the patient's version, of hard complaints, was, for the most part absent. Then. You have what we call the Galini case reports. This. Introduced. A more conversational tone. Into, the case reports, and he. Galan. Often described his work in the his doubts his tentative, diagnosis, and his. Interactions. With other physicians as the disease unfolds. Some. People believe that in the Middle Ages. Men. Method. In the Western world was dormant. However. There was a. Increased. A lot of information, coming out from the Islamic, medicine. And those. Case reports were, similar to both the Hippocratic, and the galini, case reports, and. Most. Of those case reports adhere, to. The. Galley Niek ideas. Of having. A conversational, tone but. They also put more emphasis on patient, subjective, experiences. At. The same time. Physicians. Were dramatic, in the way they, wrote case, reports, and for example in the a case, reporter, appeared any Philosophical Transactions in 1739. Had. A title saying. A girl three years old who remained a quarter of an hour on the water without, drowning. In. The 19th century case, reports there's less with potential, accounts. Of their. Illnesses, and more, technical, terms were introduced, into the case reports. They. Were more organized, and having. Sections, like demographic, details of the patient and outline of Nicolle course of events. At. The same time medical terminology, became. More prominent. Similarly. Looking. At cancer patients, the, history, was. Pretty. Much the same and mild, genocide. Eloquently. Described, case reports, as the first line of evidence where everything, begins. Some. Of the earliest case reports, of incurable. Breast tumors were also, recorded in the ancient Egyptian. The, papyrus wreck records. Of the Asian Egyptian, medicine. So. What are the potential rules, of case reports and case series. One. Is recognition, and description, of new disease in. 1999. The West Nile encephalitis. Was. Identified. In New York City. As. A new case in the, United States, another. Possible. Rule is, detection. Of drug side effects most. Drug. Retractions. Usually. Follow, case. Reports. On. The, other hand there. Are also advantages. Or, beneficial. Things. That can come out of case reports for example. Since. Then the field was designed, as a drug to, treat hypertension. However. In the course of the trial they find that a. Beneficial. Side effect, was fine well. Was picnic was picked up which, now becomes. Which, is not benefiting, a lot of people sildenafil is, the. Trade name is a. Diagram. But it was discovered accidentally. In. The same vein you have. Antidepressant. Drugs that were found to. Be useful for. Patients. Who are having. Amin who were undergoing. Smoking, cessation because. They were found a link between smoking, cessation. And, depression. And so, antidepressant. Drugs were, prescribed, for those, patients. Case. We pose can, be useful in the study of mechanism. Of disease, for example maternally. Inherited diabetes. Associated, with deafness. This, was, discovered. By looking at family. History of, people. And was, able to identify this disease and and then, from, there one onwards they were able to. Get. Identified. The mechanism, case. Reports can be very useful in medical education, and audit it's. Also useful in the recognition. Of rare manifestation. Of diseases and you. Can also have impact, on health, policy for, example. Recently. The Zika virus or, a few. Years ago with the Ebola virus where, policies. Had to be made as, a result of the cases that, came. Into the United States so. Case. Reports. Can. Be used in describing new disease or diagnosis. Historical. A case we posted as communication, between. Physicians. And that, ultimately became. The origin of journals. Hippocrates. And. Rufus. Are officials described. Case reports of melanoma, and in. Gary of 1832, Thomas.
Hodgkin, Described. Six cases, two of which we now know as. Hodgkin's. Disease. Similarly. 1957. Then his bakit described, to. Mind the jaw. The. Angle of the jaw the African children that is also called pockets. Lymphoma, today and in. 1994, and colleagues described two patients, with a new type of lymphoma, called hepatic planning, T cell lymphoma, that, has led to more focused, research. So. We're gonna. Describe. Some case reports to, you this. Is a case, of a young female athlete, with a cute low back pain caused by stage, 4 breast cancer, are. The 27, year old lady that presented to the, office of the chiropractor, with, the chief complaint of lower back pain after warming, up I'm participating in kickball, match. She. Reported feeling some discomfort while, jogging and subsequently, having pain after. Striking the ball with a rifle the pain was, only on the l2 l3 level, with. Mild radiation, or out the right part, of vertebral, region. On. The. Scale of one, to ten she described this pain, as constant, sharp and stabbing eight out, of ten, but. There was no radiation of the pain into. The extremities. She. Had a past history of uncomplicated, low back pain during, her teenage years that was treated, conservatively. And, was, attributed. To lumbar, scoliosis. On. Physical, examination there. Was decrease in flexion and extension active, range of motion with, pain in the upper lumbar area and there, was +4, tenderness on palpation. The. Patella, and Achilles tendon reflexes, were 2 out of 4 and the, padeen ski and lower extremity, cleaners were absent bilaterally. The. Muscle testing was, similar. On both sides and. Around. The paraspinal muscles there. Was increased tone, at. The level of the complaint however. There was a positive family history of, breast cancer in, the, patients. Aunt and grandmother. And, in. Previous here she had routine, mammograms, to observe assists, in her, right breast. At. The time of presentation she had not had that screening, for that particular year yet. So. A diagnosis, of lumbar sprain, and strain was, made and. Radiographs. Obtained to rule out spondylolysis. Did. Not reveal any signs of fracture, of dislocation. However. After, he died miss Mosley when they look back retrospectively, they. Found out that there were subtle nuisances. There. Were visible on the vertebral body, and the left petty good that they are missed initially. And. You. Can see on. The arrow we. You you, need the eye of faith to see it is slightly loosen. Here and around, the Pentagon same, thing here so. They. Are. With. Soft-tissue mobilizations. To her lumbar and hip and she, was placed on conservative, treatment plan for two weeks at. The same time her employers, physician, prescribed, oral. Anti-inflammatory. Drugs and, physical, therapy, which, he had to strengthen the core musculature and, increase the, range of motion. Two. Weeks after she returned to our chiropractic, office. Because. The signs and symptoms did not change and an, MRI scan, revealed, a two point, two centimeters expansive. Lesion in the left, l2. Vertebral, body with associated, overlying, vertebra, superior endplate concavity, focally, and there. Were differential, diagnoses of different, things osteoblasts, Umar giant, cell Timo pathologic. Fracture, but. Actually disease of unknown origin, was made. And. So you can see here. And. Here. The. Tumor you can see and spread. Into the pedicle. So. She was recur at a time she was referred to an oncologist who made diagnosis, of stage 4 disease breast. Cancer, she, had an ultrasound, and mammogram, guided, by o-cedar reveal. The cancerous tumor in the right breast. Tumor. Metastatic lesion were discovered, at the c67. Spinal, there was variable, scan and MRI, the. Tumor was a, hormone. Receptor positive and her2 negative. Interestingly. The original, sis was found to be benign so the tumor was below, the, original system of monitoring over the years. She. Was treated with letrozole.
Differ. RI brands, and far Sodexo and she had a right lumpectomy. And axillary, lymph node removal in, 2016. The. Spinal, lesions diminished. However, there was a metastatic. Lesion, that was confined, to the liver however. This year she, began a trial of Saluda and she's currently active, in exercise, participating. With training on polling. This. Of a lady who has. Squamous, cell carcinoma, of the tongue during pregnancy, the. 29-yard, lady in. A third pregnancy with, two children she, was referred at 14 weeks gestation. To. The Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery service, with biopsy, proven poorly. Differentiated. Screaming, cell customer, with perineural, invasion, of the right song in your area of era through leukoplakia. She. Don't have any history of smoking, and she consumed. Alcohol. Occasionally. Before. Her pregnancy, so. That's the area, that. Was bio see the lesion that and, that she, had custom of the tongue. MRI. I, imagine. Depicted, an endo fatigue mass of the, right song approaching, the midline and the. Genu. Closest muscle, on the right hand side. Was. Involved, with prominent its. Lateral level, to a leaf node was, noted. So. The clinical and little radiological. Diagnosis, she was diagnosed as did she, for a n1i, mxo. And. That's. The MRI so he can see the tumor there. They. Discuss the management, options, the, patient wanted to continue her pregnancy, and. At. 16 weeks gestation, she underwent, a, right Amy. Claw said to me and, bilateral level one to four neg dissection radio, for humphrey flip reconstruction. Free. Flap reconstruction and. A tracheostomy. So. You can see the when, they this, was the excise part, of the tongue and, this. Is what it looks like after, they repaired using the flop. So. She added, dissection on the opposite side because. The malignancy, was encrypting the midline of the tongue, she. Had infection, that was treated postoperatively. And. Pathology. Report, revealed that the net imagines. Of the mass. Was negative, for carcinoma, however. Two, lymph nodes were found to be positive, for. Regional, metastasis, with extra capsular, spread at, the. Same side of the tumor level four and on the other side level, one and. So. They had to change. The staging. Of the disease. This. Is histology, that shows you the breaking of the capsular, and the tumor. From. The lymph node. So. After discussion, with the, maternal. And. Fetal. Risk, she, had. Adjuvant. Chemo, radiotherapy, on, post-operative. Day 25, she had 60 grade to the operative bed and 60s gray to. The sides of Regional metastasis, and she. Had weekly, carboplatin. She. Had. Two-man. Therapy was completed 26 weeks of gestation and, the, estimated. Fatal dose was, $0.07, degree of radiation. She. Had serial or ultrasound, scan performed, to and evaluate. The. Fetal. Growth and is, just a picture of the. Lady. Showing. How she was treated with radiation. The. Ultrasound, depicted, appropriately. Grown fighters measuring. At. The 22nd. Percentile. I trained three weeks gestation, but dropped down to the 36 percent I like 31 and 37 weeks, she. Had a life for male infant, delivered. Vaginally at, nine weeks three. One one eight grams. One. Year after modern, child. Are doing well with no evidence of recurrence, so this just shows the. Growth. Over. The period of the, pregnancy. This. Is on the case of an 18 months old girl, I say. Yolk sac tumor of the abdominal, wall of an 18 month old girl she had. A small round, table kitchen aslam. 1.5. By 1.3, by 0.8 centimeters, of the abdominal, wall in a right. Hypochondriac. Region, the. Tumor was connected to her skin and histology confirmed, the yolk sac tumor, showing. A micro, cystic. Reticular, pattern with positive staining staining for, cytokeratin. Each as. Well as cytoplasmic, granular, staining for alpha-fetoprotein. So. That shows you the histology understanding. For alpha-fetoprotein. During. Surgery, the borders, were not clear of tissue. And she. Was stages, stage. 2 according to pediatric, oncology group the. Alpha-fetoprotein was. 57. Normal is really less than 10 nanograms, per mil three, weeks after resection, and dropped to 50 nano gram per mil one month later the. Bitter subunit, of the human chorionic or and atrophic was normal.
MRI. Of the abdomen was normal she, was followed up with cereal alpha-fetoprotein. One. Year later she had a recurrence, one point one centimeters and, the. Alpha-fetoprotein. Level, was 29 era grams per mil MRI. Of the head neck thorax abdomen did, not show any, any. Masses, here. At this time they had a wide excision, of the. Lesion that confirmed that. Mrs., by pathology, so. That's the. Lesion. There. You. Can see the you would imagine it and here. On MRI. So. This just gives. A a. Graphical. Representation. Of. The. Measuring of the alpha pto protein. Before. I came back to normal. So. Five years she's. Fine. Two. More free. Without. Any remission. This. Is the case of nivolumab induced. Hypothyroidism. And selected, pituitary, insufficiency. In a patient with lung adenocarcinoma, as, a, six year old male patient that, presented with, a soft tissue. Edema. In the right cervical, region dozen, of 14 she. Had, a history of 86 back years and was. A social, alcohol, consumer. CT. Scan identified, a 2.6 centimeter, mass in the right upper lobe of the lung along, with, abnormally. Enlarged mediastinal. Lymph nodes without further evidence of distant, metastasis. Biopsy. Was confirmed, by Brooke bronchoscopy. Was. Still just 3e, and. Beijing. Are concurrent, chemoradiotherapy. With. Cisplatin. And 54. Degree of. Radiation. That. Was, an impartial response, according, to the resist criteria, and. Surveillance. City majors, and 16 showed progressive, disease with. Enlightenment, of timon, mediastinal. Lymph adenopathy, with. A new supraclavicular, and, cervical lymph node block. So. Decided a second line of. Chemotherapy. That, included, intravenous, nivolumab. Following. The eleven cycle, which. Then developed symptoms, of dizziness gait, instability. Fatigue. Anorexia. Withdrawal. Periodic, confusion, and reduced alertness. Physical. Examination discs loose and cool edema, and bradycardia, and, no focal. Neurolo
2017-11-30 12:43



Very informative visual aids.