210521 Introduction to SAN storage
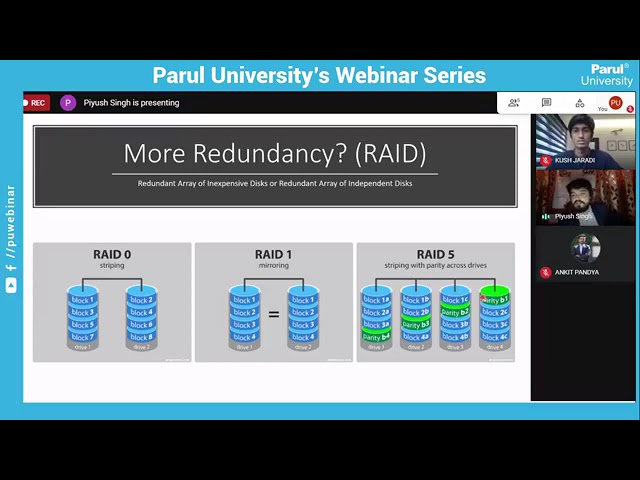
afternoon to each and every one of you who has joined with us today so today we have a very interesting session and i'd like to brief you about our expert speaker today who is joined with us today mr pew singh he is a storage specialist in ibm um we all know about ibm it's an american based mnc which is the leading cloud platform and cognitive solution company and mr pewsing was also a senior former senior analyst in hcl and uh cloud operations analyst in essential and i think our today's topic is quite curious and interesting which is sand storage so over to you so now hey thank you so much thank you so much for having me uh first of all bio university thank you so much ankit and uh yes we'll try to uh look into the topic that we're going to cover today the topic will be uh storage area network or sun so uh that is my expertise uh like uh in ibm or you i would say like uh for the past seven years so something about me i have about seven years of experience in iit industry i started my career from hcl technologies uh way back in 2014 for three years i worked there and then i joined accenture solutions and currently i'm working ibm so so as you you know as you progress in your career like you will have to work in the different different technologies if i like to summarize uh the type of work that you would get once you move into the iit industry once you try to move into the it industry uh so like you will be either a software engineer or an infrastructure engineer so if you're a software engineer you can either be a developer tester or anything and if you move into infrastructure so that is what we are going to cover today and what is the role of infrastructure engineer and what are the things he would cover and um what are their expectation and what can you expect from the id companies that we are going to see now so uh how it works like um suppose if you're hired for one it industry so uh suppose uh let's let's take an example of ibm only so you're not going to work directly for ibm so there will be different clients under ibm for which you are going to work so like this example let's take an example of any any big uh multinational company like um for example like britannia or you uh like pepsico or emirates so they're more their main focus will be on um emphasizing on their business like uh if if that is pepsico so pepsico will be more focusing on the you know product production of their snacks and you know uh beverages and uh like emirates will be focusing on aviation so they see see they are like a big multinational companies and they'll be having lots of lots of data to store that they too need uh you know it infrastructure to keep their data and keep their network like they need to have their like all the details updated like uh for example suppose we have emirates so they would need um complete information of what flight is you know uh like uh flying from which place to which place details of the passenger and everything so they will need id infrastructure like the so they are uh they will hire some i.t experts or they will reach out to it experts and uh they will give their business to that company for certain amount of time so they will outsource the id uh infrastructure if you see here so um so how it goes like suppose if there's a company that i own like it's a big multinational company and i would i like to you know give that project to some other uh i.t industry so it will go through a bidding process so i would select uh like three four companies like uh suppose uh i will see like how is their infrastructure how is there you know uh previous performances so according to that i will uh try to give the you know my business to those companies so i will there will be a bidding session there will be you know companies joining that session and um they'll bid for that project for a certain amount of time okay they'll say okay i'll give these many resources from our company and they will be working for you under our company like they will be on the payroll of the iit company only like you if you join uh suppose uh oppose ib suppose ibm so you'll be working for ibm but uh like you will be on the payroll of ibm but yeah you'll be working for different different clients that that ibm supports so whatever uh infrastructure whatever bidding uh they the company find suitable they'll give that project to that company and um for certain amount of time like like there'll be a a like uh the project will go for like five years or seven years like that so there will be a fixed tenure and uh yes so as i told you like you will be working for a different client under one id company so yes you will be dependent on that project so suppose if there is a project for five years you work for five years in ibm and now you are trying to move out of that like the project is trying to move out like they are looking for some other you know other company that is more feasible for them so you will be moved out of that project and internally you will be shifted to some other client like who ibm owns or like if there's a new project coming on so we move to that project uh according to your skills so that's why you need to you know keep your skills uh updated and uh initially you'll start definitely you'll start with one um like one skill only but yeah as you progress in your career you'll be seeing different different uh technologies in your path so what is the role of i.t infrastructure engineer so they told you infrastructure engineer like you'll be part you can be a part of a storage team server team network security cloud etc so uh different different teams have different different responsibilities okay so if you're part of a storage team you'll be responsible to manage the storage the storage switches that we'll be covering uh in the session you can be part of the server team you can handle like linux unix uh different windows servers in part of network security and cloud as well like different different team will have different different roles and responsibilities but as you progress in your career you need to have if not if you're not if not expertise but yeah you should need a good knowledge about all the other technologies as well as you progress if i move forward so why do the company needs need storage that is the one question that arises so uh there's a limb uh so in the like layman language suppose um there's a server server you can say it's like a storage uh like a computer suppose you have a computer okay you need storage so you'll be having your internal storage connected to code to it so you'll be having like 500 gb or like one terabyte of uh space so that will be sufficient for you to keep your data and stuff like for but big multinational companies they'll be having like a tv tvs of data coming every day so that will not be sufficient for them so they will need an external storage box to be connected to their servers from where they can access that storage they can keep their data and yes they should be uh like assure like the data is safe even if there's any fault but still the data will be intact and uh they can retain the data whenever required so that is why there that's why this storage box comes into the picture and there are different type of type of storage box that will uh see uh going forward so like as i told you like there will be different applications that will be hosted uh this example suppose we have a flip card right so flipkart is one application so that will be hosted on any server in the backend okay like not one server like there will be multiple servers uh um and that server will be connected to a storage box that will be uh taking the data and whatever data you have your information everything billing everything will be kept on that storage so now most of the companies are opting for cloud and what is the difference between cloud and physical storage uh i would say that will uh come to know going forward so they'll be having different application that is hosted on uh your servers and that server will be taking storage from that storage boxes that will be connected or standard storage and ask storage and depending upon their need will come to know and uh yes uh suppose uh like i i like to share one more thing suppose there is a some need of uh like what is if there is like a huge load on servers at one particular day or like two days or three days uh in an year suppose in a year like suppose if you have a big billion day sale so there will be lots of lots of users you know rushing to that applications so they will need more servers to run those applications so here cloud we have an option to auto extend the you know the number of servers so so that the load will be shared and you will not see the flip card or any other application like that uh going down so they'll be able to share the load okay so let me just move forward ahead so we have three type of storage that you'll be dealing if you're part of a storage team so you can work with uh dash storage uh that is the uh nas storage or samsung will come to know uh about them uh going forward so that's like you're directly attached storage nas is your network attached storage and san is storage area network that will be focusing today okay talking about das das is like something uh that which is directly connected to your system suppose uh you have your external hard drive that is connected so uh that will be a directly attached storage to your system it will be high performance because it is directly connected we do not have any network network in between so there will be less latency and high bandwidth but the thing is that you may lose your data anytime like if there's any connection uh issue you will lose your data so that is not feasible for big clients like you can like if there is a small business they can definitely go for a dash store yeah i like to introduce one more term like uh to be familiar with you guys so like we have um our data center like data center is a physical location where all the storage devices all the network devices all your switches everything will be uh kept and connected into a network so uh that will be one physical location like for uh one project there will be different different um uh data centers around the globe like they'll keep one data center in some like suppose in u.s and other you'll keep in some other place in u.s only so like this just to have a you know dr side or recovery site suppose of one there's one some disaster in one place so that their data will be there intact in the other location as well in i'm talking about the physical uh storage that we're going for so this is nas we have a network attached storage so nas and sand both are like equally you know in demand in the market depending upon their need uh the client can go for the nas storage or the sand storage nas tools basically uh works on the your ethernet network so that will not be you know very high speed network but yes different different uh computer devices different different uh devices can be connected over the uh shared uh shared network so like the storage uh they can access the shared storage from multiple multiple systems that we have in the network so it's easy to you know extend we have good scalability we can add as many system as we want depending upon their you know uh obviously the bandwidth and the network we can attack we can have multiple devices connected but yes still they will like there is a like a redundancy issue like uh if there's any fault in the network so your you may lose access to your data storage like nas storage will be something like uh a share drive as you as you say like if there's a google drive shared with you and you are sharing that drive with uh three more users so all the users can see that particular drive as the as you know a shared drive they can access that and if they have permission if you give permission to that storage they can also edit that data edit the you know files over there they can upload the data uh that is all that's they can do so this is something like but yeah it will be on a local area network like a lan network so that's how it differs from our drive or something and now coming to our topic main topic that we have stand storage or storage area network so san is like a high bandwidth uh high performance uh network that operates on a fiber channel network as we saw in the previous slide the nas storage works on a you know ethernet network and the sand storage works on a fiber channel network it is a fast high bandwidth storage and when you know the big clients they they they they they need the data whenever they require like they need to you know have the high bandwidth in the network and with uh least impact to their production like if there's something down or say there's some issue they still need to have the data with them all the time 24 cross seven they will rather go for uh san than nest so uh why would they choose they go for nas sorry the san instead of nas i would i will just try to demonstrate here so in this picture if you see there are the servers here these are the windows linux and unix servers uh in simple terms you can say these are the computers okay that will be having some applications the client based application that will be running like there will be multiple servers in in the environment like you're seeing just three servers here but in our environment we have thousands of servers so they will have different different applications hosted on them okay uh yes definitely the client uh applications and they will be connected to our storage area network how they are connected i'll just demonstrate here so uh rather than having a single mode of connection like if this system wants to access the data from this particular box this is the single mode of channel if there's any fault in this channel so he they will lose the data then and there but here in san what what it goes like how it goes like uh you'll have a different path of accessing a particular data so your data definitely will be stored here this is the disk array or your stance sand storage box okay they'll be having physical drives in them and yes the drives can be can become faulty they'll be you know uh loss of data for certain amount of time but if we implement it here they'll be having redundancy within the storage box they'll be having redundancy here as well in the network so the client will not lose the data uh for even for you know a moment so like they can access the data all the time meanwhile if there's any fault in the drive or we can replace the drive and get it fixed and then they'll be up and running again but yeah client will not see any loss or impact of data so if if this particular server supposed i'll just keep track on the time as well yeah suppose if this particular server wants to access uh a storage you know if they want to keep the storage uh keep the data in some storage box that is here so what they'll do they'll be see there'll be uh two parts or multiple parts of communication here they can this is the sand switch these are the sand switches okay switches switches are used to provide the redundancy okay we have a tape library as well in the network you can see so if there's any uh backup that that the client wants to take they can take the backup and keep it here okay and that will be you know that will be in a cheaper solution for uh you know backup we can take the gap back up on the storage box as well your disk array as well but the thing is that it will be very costly because yeah san is costly so if you want to take the backup and the if you want the backup to be there there and if we need it we can retrieve it like in some certain amount of time we have time to retrieve it like there's a no hard and fast thing to do so we can keep the data over the tape libraries as well so if this client wants to access the data they can go from this channel this path they can go through that this sand switch and this this sandwich is connected to disk array so they can access the data from here also there's one more path like see if we go here there's other sand switch from here also they can access the data here and these are the you know your different drives that we have these are the logical unit number ones that we call them and if we move forward as i told you there are two parts of communication here two parts of accessing the data and uh this is the like basic scenario like if you are seeing here in the sand network it can it ranges to a n number of you know uh paths that we that we can have like this is in the big environment we'll have not just two switches we'll have uh you know hundreds of switches connected and depending upon the you know how much data they need and how much you know big their infrastructure are is so on depending on upon that they'll be having multiple stands which will having more than two parts connected to a disk array just in case suppose if there's any fault in the network this is all this is only just a cable suppose if there is a fault in the cable there will be different ports connected here and they'll having ports here in the server they'll be having port obviously in the switches and the disk array suppose there's any fault in in this port or this port or this particular wire so uh still the client will be having access to the data from this part the path number two so that is why where the client needs you know data to be available all the time they will go for the sand model okay so what is the difference if you like to summarize so san versus nas nas is basically you know used in the small uh industries small business and uh big business uh always you know try to go for the sand storage and standard storage is definitely more expensive and uh requires more administration that will try to cover it in the session like what all the you know basic administration that we perform here in the sand and yes we that is the main reason the client goes for the sand storage uh the fault tolerant network that provides uh sand so they'll be having redundancy like if there's an apart down yes still the data will be accessible to the client so this is this is one thing uh for the main reason why we go for the sun storage okay so these are some of the leading sand products and vendors like we have the you know uh stand storage box from the dell we have hp hitachi ibm netapp and uh four switches the two famous uh sand switches that that they offer are like uh from brocade and cisco they have like the basic functionality will be same but yeah the operation will differ from model to model like if suppose if you go for uh power max or if you go for like other hp 12 hp we have like different like nimble and we have like different xp p90 500 different different boxes we have so depending upon the model and depending upon like um uh like depending on basically it depends on the client need what they need and the type of data they want to store the amount of data they want to store the amount of space they want they can go for the different different models and yes depending upon their support as well if you opt for you know these storage boxes yes they'll provide some support because but yet yes it will be chargeable as well if it if it comes in the contract they will be ready to support certain amount of operations certain operations that they can okay let's move forward and yes if you talk about the data centers they can be either in the um the ibm uh infrastructure the supporting infrastructure or it can be in the client infrastructure as well like the suppose if this uh there's a project like britannia and they did not want to they do not want to you know give the the data in the other data center so they will they'll have their own data center and we will be just managing that but there will be scenario as well where the the offering team will be having their own data center the ibm or hcl or other companies will be having their own data center where they will be keeping their data so just a little bit of idea about how the you know the network works here in san so uh suppose there's a new host that is connected okay and they want to connect to one storage box they want to utilize these storage that is there so see as you can see here there can be multiple you know servers that can be connected to this particular storage box so there will be the storage that we have is will be shared okay it will not be dedicated to one particular host will be a shared storage because it has it has a capacity of you know multiple terabyte or petabyte of storage it depends upon the vendor to vendor uh for sure so suppose this is a new host that that that wants to connect with the network so how it will be connected so there's a process called zoning so zoning is basically uh you know virtual connection between the ports so how will this particular storage box will know like we have a new host connected in the network and they want to access your data or you know they want to keep the data over there so for that process only we perform the zoning and zoning will be performed on these sam switches as you see here in between so uh like you can go for the gui as well you can go for cli command line interface as well we have both so whatever suits uh we can go for that and we can perform the zoning so what all components is required here is like suppose there's a host okay the host will be having multiple hbas or host bus host bus adapter so hbas are like you know and it will be used to connect to the network that we have the sand network and this sam switches will be having uh the ports okay it will be having the storage box also will be having ports the storage box will have basically uh your controllers okay these controllers will be having your uh storage port or front-end ports that is called as fiber channel ports as well so what it does like it is used for the connection so what is controller basically control is like your processor and it contains of your cpu your cache your network everything is like you know this is not just a simple box like it will be having its own memory it it has destroyed boxes has its own you know fan your your you know the power supply and the what not like your cache everything so it can operate uh here we can operate like as a single system we need to log into the storage box very often like you need to perform if you need to allocate space and all so it has its own processor definitely that that is why we are able to log into that and you know perform the all the operations and we can see like what all space is allocated to which host and all and suppose there's a new host that is connected to the network and it wants to access the data from this particular storage array so this will be having its hba host bus adapter and this will be having one port this will be having port this will be having this uh port so we log in into this uh your sand switch or fiber channel switch if you see here and we will take the port id so what is this port id everything in the network in the in the it industry it infrastructure everything every port and everything will have its unique wwn or www id what is called it is like a worldwide name it's called as worldwide you know uh identifier so it has a unique hexa uh not accelerated like yeah it has like a uh alphanumeric combination of you know characters that will uniquely identify that particular port that we have in the infrastructure so if if that if you want to perform zoning we'll have to pick that particular wwn that uniquely identifies okay this is this uh hba of this new host that is connected here we'll pick that particular wwn we'll pick the wwn of the storage array port as well we'll create a single zone so that it you know uh come to know okay this is one zone so now they are connected they are into one zone this is a lengthy process that we can cover later on that's why i haven't you know kept in this session so these two ports will now try to communicate with each other they'll have one zone created and there'll be one more zone created between this port and this port so that they come to know okay this is the storage box from where we need to keep the uh from like where we need to keep the storage and uh from where we need to access that so this is the zoning process that like a virtual virtually defining you know which port will access which port like that you can say talking about the components that we have uh in san storage so uh so this is our like host that is uh in the network okay and uh it it is connected to this you know uh your storage system okay this is suppose a storage box that we have okay so um this storage box uh will be accessed through the storage network they'll be having front-end ports in this storage box as you see here these are the front-end ports which is which are used for the connections and the back and forth will be connected to the physical drives that we have in the uh your storage so this uh data actually will be stored in that physical drives that we have but your front-end boards will be used for your connectivity as you see these are the ports and these are the controls which i talked about they'll have the uh you know cache network and everything comprises compressors of everything and yes these the the the depending upon the you know the model there can be two controllers four controllers or to provide the redundancy so if one controller is down other controller can take over so we need to have the at least one controller running up and running all the time so if one control is down like it is critical we need to contact the vendor we need to go through the process like you know there will be different different process uh defined either we need to go for the there's something like a change process we need to get the approvals from the lead okay this is the fault that we have in the environment this is the something like any any configuration change that you want to do in the environment we need to have the approvals there's a certain you know approving team that uh we need to go through there'll be you know cab team like change advisory board meeting will be there so you have to put your uh you know change over there changes something like uh you know uh creating a you know artifacts and what is the fault that we have in the environment and what we need to do to fix it so all these steps will be mentioned there and we'll have to have one scheduled time because we cannot just go on and operate at any particular time in the environment basically something which is impacting so if there's something that is impacting to the environment and so that will be performed over the weekend or something like uh during off business hours like if there's a business ours suppose if uh a client operates from suppose eight to five so we'll try to do it uh after five so that have so that we can have least impact there will be certain scenarios where we need to you know reboot the host as well suppose so that host needs to be up and running during the business hour so we cannot perform at that particular time we need to perform it uh during the of business hours so that is why we will get the approvals we'll mention everything like this is the issue that we're going to you know tackle and this is the steps that we're going to perform and we need to reboot the system and things like that so that will go through approved window okay they'll they'll see they'll be you know board members that will be sitting there and they'll see okay this is the uh operation that they need to go and that we're going to perform there'll be different different application owner with them so like uh there'll be different application owners and suppose this is the you know uh host that is going to be rebooted so for that particular host there will be different different app owners so that those app owners will be uh responsible to give the approvals if you want to go ahead or not so if they give approvals we can definitely go ahead and you know perform the activity in that particular time period so yes as we were talking they are controllers and if there's one controller down definitely we need to look into that and we need to you know get it fixed as soon as possible we can have multiple controllers we can have four controllers it controls depending upon the storage box that we have so these are the backend board that are connected to your physical disk we will talk about more uh about you know the processes that we handle uh going forward if the time allows i think it will so let's keep going yes so we talked about redundancy in the network front end like in the network part suppose if there's any you know one path goes down we still have the access to the data as you can see this is uh the the back end like in the back end we have the physical disk so these disk also will be having uh redundancy okay not just the you know the front-end port like suppose if the data is stored in one particular drive and now and the drive goes down there's any faulty drive so still the client needs to have the data with them all the time so we need to implement a raid or a redundant array of independent or inexpensive disk we can call either of them so we need to implement raid to have the redundancy over the data as well so that if there's any fault with the drives as well we can still have the access to the data so if i talk about few of these like rate zero is not basically like uh it's in use like we cannot uh like practically it's not uh the clients are using so like raid 0 is just basically striping of data so suppose this is one physical drive that you have the other drive that we have here drive 2 and um uh so data will not be written like if you if you have like suppose uh 10 mb of uh you know um data some you have a 10 mb of you know some file pdf file so you cannot just go ahead and store that particular file in one particular drive in the back end how it goes like it will be the data will be divided into different different blocks chunks uh chunks also you can say like different blocks also so these blocks will be written across the drives you know just to have redundancy and so it will not be stored in one particular drive suppose if you are storing that drive that particular data in one drive only okay and if drive goes down so it will lose your data so for that instance it will be uh implemented over raid you'll be having the data will be divided into different blocks and it will be stored across the drives so rate zero is basically you know striping the data like one block will be written to one drive other block of that particular 10mb file will go to the other drive like that block three block four like that so uh it is not like basically in use like if if that one drive goes down yes you'll lose the uh data of the this particular drive so raid one comes into picture grade one performs uh you know there's no redundancy but you still yeah yeah the data will be accessible very quickly because yes it is distributed and now it can be accessed at any time like without any you know any major latency rate one is like providing more uh redundancy it is like this mirroring of data rate one like if one of the block will be written to one drive the same block will be written to the other drive as well so but it it is it is you know having it is feasible in terms of you if you say like um accessing the data the data will be there like suppose if this particular block uh or particular drive goes down you'll be having accessing access to the complete data like block one two three four that comprises uh like that that makes up a particular you know file that you saved here but still it is not feasible because it will be very costly because you need to buy two set of drives for uh you know what could have been saved in one particular drive only so that's uh how like raid 5 raid 6 and raid 10 comes into the picture that we will talk about raid 5 here so raid 5 what what it does is like it like striping uh that we see here like different blocks will be stored in different different uh drive so same way it goes here block one block two block three and we have parity as well so what parity does it will hold the information of this particular complete set of drives okay like it is parity b1 so it will store the data uh information about this particular drive so even if one particular drive goes down completely it can still be recovered using these parity like suppose if this particular drive completely goes down it can be built up using this disparity and at least we need to have three drives to implement this raid five raid six is similar just need to have we'll have double parity you know to have more redundancy we will have two parity bits so these are the actually the drives actually the data that we are going to store and these are the parity drive for redundancy okay so yes talking about clouds i am i'm amazon certified solution architect i uh like the clients now need uh cloud resources as well because uh many of them are you know opting for uh a cloud technology over the you know other uh physical infrastructure why they need uh cloud technology uh i would say like uh cloud is like much cheaper to implement initially initially only because uh they will need you know uh the everything will be there set up uh with the with the you know the vendors and you just need to in uh start utilizing the resources without worrying about like okay we need to set up and everything so we can just start utilizing the uh resources that they have to offer we need we not need not to have our own data center we need not to you know uh have you know just big uh teams that we have everything will be there with the cloud and we just need one person two person three person like depending on the size to manage those data so cloud is like uh you can say like initially it will be you know cheaper like as i mentioned like small upfront cost will be there and uh it works on a pay as you grow model like if uh initially it will be cheaper but yes as your data as you as you start utilizing more and more resources from the cloud you will definitely have to pay for their uh users and it is easily manageable as i as i mentioned and the data will be definitely with the vendor so that is one drawback that for that is one reason uh uh why most of the clients are setting back with the your physical or on-premise infrastructure because that if they will be different uh security level that we need to uh manage by our own and there will be certain some uh you know certain set of sort of configuration that will be done from the vendor side so just to have more security uh they uh if you the client want more security they want more stable infrastructure they will they rather settle down with the on-premise infrastructure you but yes since cloud is the future and like many clients are moving to cloud we we like uh as you know start if you start your career as a as an it infrastructure i highly recommend they know in from initial stage only you try to you know get uh certified in one of the cloud technologies and definitely they'll they'll have something to offer you like uh going forward like for uh in in amazon like we have like these are the big cloud providers that we have we have amazon aws we have gcp google cloud platform we have uh microsoft azure and we have ibm cloud as well so yes depending upon you know uh the needs we can opt for any of them and uh yes that is how it goes you can get certified it's very easy like you can uh go for any courses online you'll see and you know you can get certified it will help you uh in your in growing uh with your career like uh along but yes for that also we need to have you know good infrastructure knowledge once you are good it is basically you can say the cloud is basically it works as a uh it is uh id infrastructure or a cloud like there's someone else managing it it is it will have their own you know ui but the basics will be the same different will have this storage we have network everything but yes it has a different ui definitely because uh it works on operates on different different platforms like amazon cloud and gcp and microsoft azure so this is how it goes so that is what i had to cover in the session uh and um think if there's any queries i'll i'd love to you know hear back and uh like try to answer and yes if there's any query at any point of time if you need any suggestions because i'm here in this industry from the past seven years i know like what is in the market what is in the demand and i know what helps what may help you to grow as a you know i.t engineer so you can
definitely reach out to me at this this is my email address kstepalan gmail.com and i would love love to connect with you all so i think we have some questions right here yeah there's one question from jaya patel so the question is that um are the backup centers attached in the same network or are they some at some other geographical locations yeah yeah thanks jeff for the question so like uh as i mentioned like tape libraries libraries are the one of the you know a backup solution that we have so it will be there in the data centers where we have all these storage boxes and everything attached in the network so it will be there and it can it can operate remotely as well we can have the backup we can have the you know uh your physical infrastructure we can have the data backup taken over the cloud as well so it can be with the vendor we can take the backup uh you know uh remotely as well so both the things will work and one more question that he asked is what are the security layers and structures in the most basic layer of sand storage yeah okay what are the security layers so security layer as i told that is the one thing that i covered like that was uh zoning so zoning is the one that provides your security so that okay so if we want to restrict the data that you have to one particular host if you want the data to be accessed from by that particular host only if you don't want to be you know accessible to other hosts that is where the zoning comes into picture and if i uh uh go into deep like there will be two type of zoning uh soft uh soft zoning and hard zoning so soft zoning as i mentioned they will be all the ports will have their wwn or worldwide name identifier so that is the that they are used for your soft zoning hard zoning works on the port bases like uh they will you'll not need not to mention the uh that particular wwm you just mentioned the port okay this is the one port that belongs to this particular host this particular port belongs to this particular storage box so um that in that way it will provide more secure you know layer uh to access the data so if you want to have more security we can go for that hard zoning but usually client goes for that soft zoning as well that helps in the that will be easier to manage and configuration also but yes i did hard zoning as well so yes this is one plus security level that we can say we can have and yes as i as he mentioned this question about the backup so we can as i mentioned like we can go for the backup or the cloud as well but yes it will be very costly because backup will be something like you know there'll be you know plenty of data terabyte or petabyte of data as we progress usually backup the client preferred to be you know taken uh on their physical infrastructure only because cloud when it grows it will be very very costly very very costly and yes we have different you know like i have experience on aws as well so yes we have different set of you know uh setup that we can do like if you want to access the data very frequently suppose they are taking the backup and every four days five days that uh they are taking back the data they are retrieving the data so that will be called as a hot data and that will be taken uh you know there will be certain set of settings to be made to get them you know access as soon as possible so that will be definitely a high cost and if there's something like there's something like cold data and suppose they're taking the data and they need very or like very often like in one year or two here they need the data they can keep it there and that will be low cost model as well so we have that option in the cloud okay so there is one more question that personally i wanted to ask is what if one server crashes uh in the sand storage so how can the data be retrieved back good question so uh like uh if the suppose as i've told you like there'll be a backup solution that we need to see like there's one thing like they can they can be fought at the storage and they can default at the networks they can be followed on the server itself so yes the the data that you can take backup uh will be from definitely from the tape library that will be attached and also like uh we can take the uh backup at the uh you know if there is something very critical like if there's particular application suppose flipkart is there it's very critical we need to be there we need to have it up and running every time so we can take the backup at the uh storage end as well okay but yes so see since it is uh it will be taking the same amount of data as the actual data suppose there's a 10 petabyte of data and the backup is being taken at the storage and also 10 beta bytes so you can see like it's very huge amount of data but still if if client wants to go for if that if they want to have it you know that much you know uh availability they want to have that so they can we can take definitely take the backup at the you know storage box as well that will be kept at the physical storage drives that i have told you okay so it will be having redundancy and yes it can be accessed very frequently as san operates over a five well terror network it is very you know fast and we can access it uh very uh whenever we require so it's uh that is one thing yeah and talking about firebird channel so what uh what customer problems does the sand solve yes so good question once again so fiber channel like if you are uh suppose uh initially if you are a storage engineer so you will have to deal with if i try to go back to the slide one minute talking about this diagram if you see if you are a storage engineer so your responsibility will be uh handling this particular box you will be respond you will be responsible to handle this particular switches that we have in the network and there will be different team managing your host as well but yes as we progress like uh after this seven years like i am like pretty much into everything i'll be managing host as well storage switches everything there a little bit definitely a network team expert will be there but yes this network what you say like in between the devices that will be managed by you so this uh this is very powerful like the sam switches it has its own cli gui whenever a port is down suppose this this uh in this uh we have seen like only one port connected here one port connected here but yes it will be having like 100 support depending upon the model and uh whenever a port is faulty okay so it has its own monitoring system that will alert the customers or like okay one but there's one problem with this particular port this is fluctuating suppose there's some issue with this particular port okay there's some issue with the cable so the connection will be fluctuating uh they'll not be able to access the data every time like there'll be some like uh drops for like milliseconds there if you go if you log into that particular you know switch and if you see the logs of that particular uh switch as as a whole like there's a command like fabric lock hyphen s for your blockade switches so we'll see this suppose this is this particular cable is connected to suppose port 19 of this particular switch so in port 19 you will see uh the date like uh the port is going offline port is coming online so within second only you will see like hundreds of logs like it is fluctuating so this this shows like there's some issue with this particular port and needs to be you know uh seen or you know remediated so then you will see okay what what can be the issue there's you can there's a command like for port show we can see the particular port there's a we can check like if there's an issue with the port will uh then engage the vendor and it will again go through that process like we need to you know get the approvals okay what is the process if you like as you start working you'll come to know okay what are the basic operations that we perform like we need to sometimes uh need to change the cable as well sometimes we need to change this hba where this particular port will be plugged in like you have suppose your uh your lan port okay so that will be having that cap over there white cap okay so that will be also there will where we'll be plugging in you know the device physically the cables physically so sometimes that will also go faulty uh sometimes you know they'll be this 12 box also will be having you know the components as i told like they'll be having uh your battery your fan and everything your drives so anything can go uh faulty okay so so for that it it has its own monitoring system so it will this uh storage array is smart enough to you know generate the logs and it will trigger we can set the you know uh particular email id we can provide okay the client email id where it will alert the customers okay this particular drive or this particular device is getting faulty so we need to uh engage the vendor and get it sorted and yes everything will have their own firmware on uh version that we need to you know the os version that we need to upgrade time to time or to tackle with the security issues we need to upgrade the you know firmware of this device and yeah storage boxes as well yes okay very well explained thank you so much sir and the last question that i had was uh you this all this all the san is about the storage right so what kind of physical storage do do you use and uh or is it partially some part of it is stored in cloud services as well um see if you talk about the like if you're being uh infrastructure engineer everything will be there in the data center it will be everything will be stored in there in your in your physical geographical locations only yeah but yes there is uh like uh offerings from the cloud vendors like uh we can still have all the infrastructure set up in your you know uh uh you know your data center there's something like gateway if i if i'm able to call it correctly and uh using that you will be able to access the cloud you know uh resources as well we can have both of them running like if you want uh the customer wants something to be you know access from the cloud you can still have that uh facility that will be connected like your device will be connected to the cloud and yes the clients can access that particular uh data uh like uh like it they'll be like no you know uh differences uh from the client client end but yes that will be accessed from the uh cloud also like if they want to have a cheaper solution of course yeah okay so thank you so much sir you explained this pretty well i mean personally for me i understood a lot about sand storage also about nash storage and dash storage that you talked about previously so this was a very wonderful session so thank you for taking out your out your time and i guess all our viewers also you know gained a little bit of knowledge about how the things would work in the in the professional field as well so thank you so much for it and thank you for watching and yeah it's always wonderful to share anything i know like uh had i not been uh uh like id professional i would have definitely chose uh this career as a teacher or something so yes if there's something i can be helpful uh please do reach out to me anytime this like i have many friends that are connected over you know using this channel only uh like who wants to learn and wants to see you know like who want to know like what is going there and you know want to have some experience so definitely i would love to share my experience not specifically in this story but yes anything like if you want like uh how to grow and what are the technologies in demand i'll be definitely there you want the links to you know study and there will be free courses all around that i'll be aware so yes i would be definitely able to you know and yes you need to keep learning so thanks thankfully light is back so yes so after the session so yes we can you know you just the main like moto is like you just need to keep going you know you cannot be sticking to a particular you know technology in itneu you can assume like you okay i'll be you know retired with this particular technology only but yes every every two years three years there'll be new technology in the market there'll be new challenges so yes you need to keep yourself updating with the technologies and the demand in the market and you need to know like what is there in the market and what you know what can keep you in the in the race so yes it's always a learning scenario so for me also like uh nowadays also we are going through uh you know your trainings and all so it's not just like uh sticking to one particular story in this story only like i i can say like a 20 plus technology that worked but but still need to learn more so as the client wants like okay we are going to have this only in the market if you are aware let me know so yes definitely will be aware we'll have to learn that you cannot just deny that so yes so that is why it works very well said indeed thank you okay so ankit anything to add yeah so uh thank you very much pierce for uh getting something new to you know discuss upon that you know this session i would definitely say would help or at least ignite our students to get something new to learn upon as kush has rightly mentioned yeah i would i must say that push had been a very nice support throughout the session as a moderator good observer yes like yeah he has been noting down all the topics so it's actually actually who actually is working a lot on this type of sessions and everything the moment i informed him that okay we are having this kind of session which is delivered by you so he was continuously searching out what exactly the sand storage is because this is something that they don't you know they don't have it in their studies in the curriculum yes regular curriculum which is there that is going on and it's great to have this kind of students who would have this kind of i can say inclination towards learning something new and yes definitely it's good to have it's great to have people like you those who are ready to share their knowledge with us and with our students specifically so that they also would you know get some dedication towards something new to work out upon because this is the field that is the id and computer no doubt i am also one of the parts i was parts but now even i uh you know shifted to something which is related to management so yeah but yes this particular session would definitely help our students to get something new to learn upon to think upon at least so that they would have something to study in this particular time when they are having nothing much going on and they are at home they would like to definitely go through with this type of sessions and yes as you said we would definitely be there always with uh this kind of queries with this uh this kind of requests from our site that yes we want you to be there for this kind of sessions for sure yeah so with this uh yeah i would like to again thank uh piers yes i would definitely thank kush as well for being the best of the moderators throughout the session and soon we would be planning certain this kind of sessions in near future uh i would like to thank all the viewers joined with us today and thank you very much everyone please stay connected and for any of the queries you can definitely reach us out whether through the email which is mentioned over here on your screen or through the facebook page on which we are having this session going on live so thank you very much everyone see you soon please take care thank you so much guys thank you for having me and stay safe you
2021-05-25