Reduce risk with Microsoft 365 access control technologies THR3011
All, right I think we'll go get started, good, morning welcome, and thank you for coming to this session. In. This session we will cover some. Of the risks that you deal with when you move your business to the cloud and how Microsoft, 365 access. Control technologies, can help you mitigate, some of those risks, how, many of you are already, on the cloud like using Microsoft, 365 office, 365, awesome, you know almost all. Of you I guess, otherwise why would you be here right, so. We, will do this in two parts the, first part I will talk about some of the access control technologies, and the rigor that we have in the data center to keep your data safe in our data centers, and. In the second part I'll also talk about a feature that you could leverage, in, your, organization. Where, you could mitigate against, privileged, admin. Threats. That that. The admins, have right so two. Parts one, part talk about how, we'd run the data center and what are some of the transparency, and control features that you can leverage and the second part how in your organization. You can run. With zero standing admin privileges, so that's how that's how will, that's. How the session is kind of planned my. Name is Anand Menon I am, a program, manager in the security, and compliance team. Most. Of the features that you see here, comes. From my team and, I will be available after, after the session for any questions, if, you have. So. When, you move to the cloud or when you take your business to the cloud what are some of the risks or what are some of the concerns that you have you, worry about data security you worry about where my data is how, my data is stored is my data encrypted, is my data encrypted at rest is it encrypted. And transit, who, has access to my data right because, suddenly before, you used to be in on-premises. And then, you saw your data you had all the controls now you're not on the, cloud and what, happens with your data right how's. The access control, control. There right that's, the service provider have unfettered access to my data so all that concerns comes in and about data privacy you worry about like the cloud service providers, data access policies, what, are the privacy policies there and, then, you worry about just, the cloud service provider sell my data like that do they use this for other commercial purposes, so you worry about that then. You worry about transparency and control you worry about who, has access to my data if somebody access my data how am I going to know right, and how can I control. The, access to that data because, it's my data right it's your data so you should be able to control who gets access to your data and then, most of you might be in a regulated, industry, so. If you're doing business with the cloud service provider you, want to make sure that the cloud service provider is compliant, with the regulations that your industry, needs right, so these are kind of the main concerns. I believe that you will have when you take your business to the cloud and. You. Should ask these questions to all the cloud service providers, that you work, with and. At Microsoft, we take this really seriously in. Fact there is nothing more important, to us than keeping, your, data safe secure.
Private, And compliant, in our data center and we, want to do it with the utmost transparency. And control. For, you. So. What, I'll do is I'll start with. How. We keep, your data safe in the data center so we meaning, Microsoft, when. You're doing business with Microsoft. 365 or office 365 your data is in the cloud how, we as a service provider keep your data safe in the cloud, so. We'll look at it from three different angles from. An engineering perspective. These. Are the people who, govern the, service right these are people you, know my team is on call and we, operate on a DevOps model, where, our engineers, are on call and we support the service so what are some of the access control, processes. And policies we have in place to, keep your data safe in the data center and then we look at the service itself how the service, is designed grounds. Up so that you get that data security and privacy and then, lastly some of the access control technologies, that we have and the, tools that enable us with that. So. Looking at the engineers, all our engineers, before they even get any access to the data center they have to have background check they, need to have trainings, they need to go go, through at least two trainings. In the FISMA training, and the data center security training they. Need to have, required clearances, if they need to operate a specific. In a specific jurisdiction and that jurisdiction. Dictates. Certain clearances, they need to have those clearances these, are all like prerequisite, right before even you get an account in the data center you need to have all that and then, they, need to have multi-factor authentication so, with, multi-factor, authentication, we, have enabled you be keys in, addition to smart cards we also have you be keys, if you don't know you be key is a capacitive, touch device so you need to be near the device and touch the, device and. It is, a way of authenticating into, the system we also have form based authentication. For. Any reason if an engineer needs to log into the data center into a machine because, if they can't automatically, recover a service or if, they need to look at what what, is going bad with the service they.
Need To they cannot use their their corporate. Machines they need to use a machine, saw, or, a secure access workstation. These are tightly, controlled, machines. And it does not have access to a lot of the other resources so these are kind of control machines which. Gets you access into the data center and then. You. Need so you have all the clearances, you have all the multi-factor authentication but, still you. Need to if you need an elevated, privileges into, the data center you need to go through multiple levels of approvals because, we operate on something, called a zero standing admin rights nobody, in the data center is an admin, in no no, user in the data center is an admin right, so every time somebody, needs to get an elevated access they will have to request for it and I'll cover how how, one, goes about that. So. Moving, from engineer to service right so engineer, we got everything covered on the engineer the background check cleared but, if the service does not support. Isolation. That's a problem right if the is the engineer needs to get say reboot the service but he gets access to everything in the data center for just doing that that's not going to work right so that's how we have kind of designed, the, infrastructure. Using our back from grounds up where if, as, an engineer I just need to reboot a service I get access to just that I get, no no, more than that right so I don't even go close to the customer data so customer data is. Lately isolated, it separate all, my data center operations, are on. This, side right so that's. That's how the, data isolation, happens and then. All. The access to the data center for an engineer it's just in time and just enough access so we didn't stop there we wanted even the tasks, or the automated. Automated. Yeah. Automated, tasks that run on the data center we want it to run in release privilege not just the user we, want tasks, also run with lease privilege so say, for example if you have a. Automated. Task that. Does. Network, matching right it runs with the least privileged, access right. It does not give you get the system level access it just gets the least privileged access even for just that task right, so. Role. Based access control I mentioned that's the technology that is behind. The. Service and, if. There, is a activity, that can be repeated we, look at ways to automate it because M 365. Is a service at scale and we, cannot add keep. On adding people as we grow, right so the way we do it is by automating, as much as possible we, run about like 70 million volt clocks in a day which. Is about like 2 billion a month right so the only way we will scale is by automating, and what. Are some of the technologies, access control technologies, that we use. Just-in-time. Access, just, enough access so the engineer gets just. The right amount, of privileges, to log into the radius Center or you, know run a service in the data center all. Accesses, time-bound, so, the. Maximum duration that we allow in case of if. There is any reason to. Access customer data the maximum duration we allow is 4 hours and. Then everything, in the data center is logged. And audited, and the. Tool, or the technology, that allows us to do. This just, in time just enough and time-bound access, is what. We call as data center lockbox, so. Remember. How I. Talked, about zero, standing admin rights so, nobody, in the data center has any standing rights to a standing. Admin rights in, so, if. I need an elevated, privileges the, way I do it is is I request. For access through a system, called lockbox, the. Lockbox does, all the checks all the basic, checks is is a my, background, check do I have the necessary clearance do I have all the required, trainings. And once. Lockbox, passes, through all that checks then, the, request goes my requests for elevation goes to a manager, it, is you, know it could be anybody in my management chain and they, will have to approve my request before, I get elevated privileges into, the data, center so as. You can see we, apply a lot of regard to access, control rigor to keep your data safe in the data center you don't need to buy any products, for.
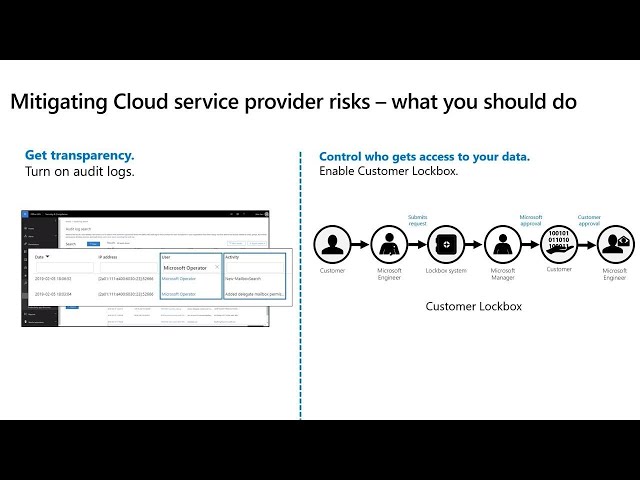
This Right so you are on em, play six file you get this out of the box right. So. But but you might be in a regulated, industry you might be in a regulated industry where, you. Know you might have to prove to your auditors, or your regulators, on any. Any, access outside of your organization right, so, that's, where you know there are certain. Features that are available to you that you should leverage first, and foremost is for transparency, you. Should enable audit logs right, audit logs is the way for you to know if there is any access that has happened outside of your organization, so if you turn on audit logs and, integrated, with your seem systems, then, you will know if a if, anybody from Microsoft has had, access to your day data, you don't need a again you don't need to buy any new products for this you get this by. Default and you should turn this on. The. Second one is. You. Might want to control access to your data right because it's your data you, want to control who gets access to your data so that's where custom lock box comes in so if you are on a g5. SKU, or if, you have an advanced compliance, queue then, you get this feature customer, lockbox right. So remember, I talked, about data. Center log box where every. Elevated, access to the data center is controlled, through lockbox, so, customer, lockbox is an extension. Of our data center lockbox so let's take a scenario, right. So. You, are a customer right. You ran into an issue with say a mailbox some. You know some one of your users mailbox got corrupted. Right and your. Admin tried to recover it they, couldn't so they raised a support ticket with Microsoft, right, so the Microsoft, support team passes, it down to the engineering team and the, engineer takes a look at it. And says Oh for, me to troubleshoot, this I need to get access to the, data because, you know the mailbox is corrupt so he probably you have to run a command that potentially, will give him, access to the data to. The data so, that's where customer lockbox flow, kind of kicks, in right. So, similar. Flow so the customer raises a request Microsoft, engineer, gets the request deems that hey this is a access to customer data request they, send. The request in lockbox, lockbox. System lock box system does all the prerequisite, checks, and then, it sends to a Microsoft, manager, for approval so, the Microsoft manager uh protects, a look at the request approves, the request and, now, if this. Is a customer data request right remember so, once the manager approves the request if.
The. Access, is for customer, data and if the customer has turned on customer, lockbox that's. When the request will now go to the customer, you for, approval so you will see any requests coming from Microsoft, it will say Microsoft engineer and then, you can approve, the request or only, when you approve the request that's when the engineer will get access to the data center so with, this you pretty, much control, who gets access to your data in the data center, so. Let's quickly, look at the customer, lockbox flow, here, so. I am in the admin center I'm pretty, sure you guys are familiar with admin, center so in admin center if I go, to. Support. Settings. So. In the settings tab. You, see that it's a customer lockbox, option. Here so this is an opt-in, feature by default this won't be turned on because by, turning this on what you are saying is, now. If there is a data access request in my organization. Somebody, from my organization needs, to approve it so you need to have a designated, approver. Added. For this so that's why it's not a man. You know default, option you will have to opt in to customer, lockbox so, to, opt in you click on edit, this. Is turned on so you know you will see this slider. On. So. It says requires approval for data access request, once, you save now. Customer lockbox is turned on what, you should do is you should also configure, who will approve the request right by default there are two roles that are allowed to approve, customer lockbox requests the first one is global, admin, global. Admins of course obviously. Can have access, the second one is a. Canned. Role for customer, lockbox called customer lockbox access, approvers, and the, reason why we have added this is because since, this is a access. Request, from, outside, you probably want your legal, team to weigh in on this right you probably want your sealer team to weigh in on this and you, don't want to give your legal team global, admin access to approve these requests so that's why you know you can, you. Can add people whom. You deem are qualified. To approve the request, to. This role customer lockbox are acts approver role and. Then. When, there is a request you. Would get an email the, global admins and people who are in the customer, lockbox approval, role will, get an email like this and if. You can read there is a service. Request number in here so this is the support request that you have created, in the beginning with Microsoft, so this is a reference for, you so you can go back and so. If you, didn't know where. This request came from that's the reference number for me and. Then, it, also says the duration, in, this case it's 4 hours and for. Any data access requests, in the data center four hours is the maximum, we do, not allow anything more than four hours it, can be lower than that but we don't allow more than four hours and then, you can also see there is a. Deadline, here they say citizenship, is us so some of the customers have jurisdictional. Laws that says hey people from outside certain, jurisdiction. Cannot access my data so it's for that so, if that does not comply. With your from internal process you can deny the request but, bear, in mind the issue, that you had will, linger, because you know you, have rejected the request now right so. So. So. This is where you will start seeing all the customer lockbox requests. You. Know there is a reference number, so. You can you can click on it. You. Can click on one of the requests that is in pending state and. Then approve the request and. It, says Microsoft has a four-hour, window for this. Right. Now the request is approved and this, is when this. Is when the engineer, gets access to your data for, four hours to troubleshoot, the issue that, you, you are having with your mailbox right so that's the, customer.
Lockbox Flow. And. Then all the things that I talked about needs to be audited like don't take our word for that right so we have external, auditors, who audit our service all the time and. We. Probably have Microsoft. Has the most comprehensive, set of compliance, offering, across. Industries. Region, global, I don't. Even know half of it here but. So. So. The. Point that I want to make is like your data, in the data center is safe we that's. That's. The most important, job that we have like to protect your data that is in the data center so. Yeah. And then, moving on moving. On to the second part this, is the first part that I talked about in the data center the second part is you, as a tenant right so I talked, about how we operate, our data center with zero standing admins but. In, your organization. You probably have global, administrators, right there, was the data that said on an, average there are about 13. Global, administrators. In an organization, right so these global administrators. Have superpowers, and they, could you. Know turn, into an internal rogue admin or you, know they could be, subject, for a subject of an phishing. Attack right and if, their credentials, are lost, then, they could be used as an attack vector and. Then, you know it could be used to copy your sensitive data to external storage. Your. Data, could be held, at for ransom, or email, words like it could be used for a large. Infrastructure. Attack. Like a DDoS kind of attack which could kind. Of play mayhem, for your business. Right so. What. Are some of the things that you could do in your organization, to ensure. That you. Operate, with like zero standing admins right in your organization, so. First. An able. MFA for admins, it's it's no-brainer turn. On privileged Identity, Manager mint in Azure ad so, this is JIT access for your roles so. As a global administrator, that you are not a standing. Global administrator, you are using just-in-time. Access, to get global administrator, role so turn that on and. The. Third thing is so. Even if you are jittered, into an admin, role for, how many other duration that you are global. Administrator, the risk still exists right so how do we mitigate against, that so, that's where privileged. Access management, in Microsoft. 365 comes in, privileged. Access management in Microsoft, reach by is a granular, task, based access so, even if you are an administrator there are certain, tasks, that you can guard, like. For example Journal. Rules right if, you are in an exchange administrator, you can create journal rule rules, and siphon your email out right, and if you, probably. Once you create it nobody is going to know right it's, going to stay there and then all the email gets siphoned out right, so how, do you protect against that right so that's what privileged, access management, gives. And I'll quickly, cover that as well so. Privileged. Access management, is just in time granular. Tasks asked access, there, is a privileged admin workflow so if you need to get access to that task you need to go through about flow just like how I showed in Lockbox, it needs to be approved by a manager, so same, workflow applies, here and everything, is audit, ready as well. So. Let's take a look at privileged access management, so the, scenario that I talked about you are an exchange administrator, you. Create a new journal rule in this case you, are getting. Your CEOs, email, or the, attackers using. New. Journal rule to siphon out your CEOs email, to an external email address, right this, this can be done today.
So. If, you have privileged, access management, in, M, 365, you, should be able to prevent this let's look at how. Right. Again, in the admin in, the admin center you. Board settings. So. You see a privileged, access, tab. In here it's turned on for, this tenant but you, can turn this on it's. A slider you have to also add an approver for this once. You save it you. Know the axis privileged, access is turned. On, now. The. Privileged access is turned on but you have to set policies, right you saw how new, journal rule it's easy to create now, you need to create a policy to prevent new, journal rule from getting access so, the way you do it is is you. Come into the PAMP screen you, configure. Policies, you add a new policy it's. It's. It's a task, because, new journal rule is a lower-level task the. Policy scope is exchanged you select the policy name again. New journal rule and. Approval, type there are two types we support manual, and auto approval, for. Critical. Tasks you might want this to be a manual approval, so that it goes to somebody a second, a, second. Pair of eyes take a look at this before approving so, you turn, this on there. Is an approver group so these are the approvers who will get the email. So. Once you create this now, there is a policy, that is in place. For. New journal rule, now. If you go back to the powershell this. Is probably the you. Know the window that a lot of the admins. Love if. I try to create the. Same journal, rule because, now i have a policy, that is set it says that please. Raise an elevated, request because this is now blocked. That. Means even if you're a global administrator, you will not be able to access this. Task right. So. The way I if. I need if there is a genuine reason for me to run this task the way I would do it is is by coming, back here I will click. On access request I will create, a new request I will say the task is exchange. Its new journal rule I want it for an hour because I need to create a create. A new journaling rule for auditing and. I save it. So. Now there is a new request that is in pending state right, now. Who. Are is part of that Pam approvers, group that I showed before we'll, get this request and they can approve it so if you I switch back so. You see you, know I've switched back to another administrator, they. Will see the same request. And they, can click on it and. They can approve the request and once. The request has been successfully, approved this. Is when, the. Admin can go back and they, can run this new journal rule again right, because we have put this under Pam. Or privileged, access manager, so even if you're a global administrator. You will not be able to you, will not be able to run certain critical, tasks. Yeah. So I was going to go so right now it works for exchange we are working on extending, this to SharePoint and teams and other workloads. And. I. Know I'm running out, of time so quickly, here are some of the resources, please. Go read I recommend, there are two sessions one, on data center security, you, know how we run operate. Our Microsoft, data center with zero trust that is tomorrow and. Then there is also one right, after that on how. You protect, your data in transit and in, and. A trust with, encryption, technology, so I recommend, that you go. For these sessions and, just. To wrap up. What. Are some of your to-dos enforced. Ufa for your admins turn. On unified. Audit logs integrate. With your same system so you know if, anybody else is accessing the data, enable. Custom log box if you are on e5 advanced, compliance, queue enable, customer lockbox use. PEM for. Jet turn. On Pam. Again. If you're an empty. 65, turn on pan for granular access control, but. For. Everything else in the data center don't. Worry we got you covered, yeah. So. That's all that's all I had I'll be available for questions, afterwards thank, you thank you.
2020-01-16