Coffee&Learn - all you need to know about LTE-M
[Christian] hello welcome to another episode of the IoT Webinar series my name is christian henke and I'm the director of product marketing at EMnify we know building IoT products is complex and this is why I'm inviting to every episode an IoT industry expert. The expert will give you key tips and tricks on how to solve technical challenges and how to scale your product and operation if you like the topic or have suggestions for a new one subscribe to our EMnify youtube channel and leave a comment now let's get started Hello from berlin thank you for attending this webinar today. We have a little bit of a different webinar format than the usual ones which we call "Coffee and learn". We just recently had several announcements and wanted to give you the chance just to interact with us and ask specific questions about these topics. So today i, therefore, invited a very special guest and colleague of mine to talk about our recent announcement of the availability of LTE-M please welcome Nhu Ho.
[Nhu] thanks christian glad to be here today [Christian] Nhu has been in the low-power IoT space for more than five years first working at Fraunhofer that invented Mioty a low power wide area network - and then also went to Beartech who commercially made my Mioty available. Since about seven months, I'm really glad that she joined EMnify and she has been a key driver behind our LTE-M announcement. Today i will talk with Nhu new about questions like the benefits of LTE-M, frequency bands, where LTE-M is deployed how does LTE-M stack up compared to narrowband IoT and which service levels does EMnify provide. but actually, the reason why we do this is we want you to provide questions that you have around this technology so please ask questions in the question panel and i will try to intermingle these questions and will ask them Nhu directly. so to open up the stage and as an introduction
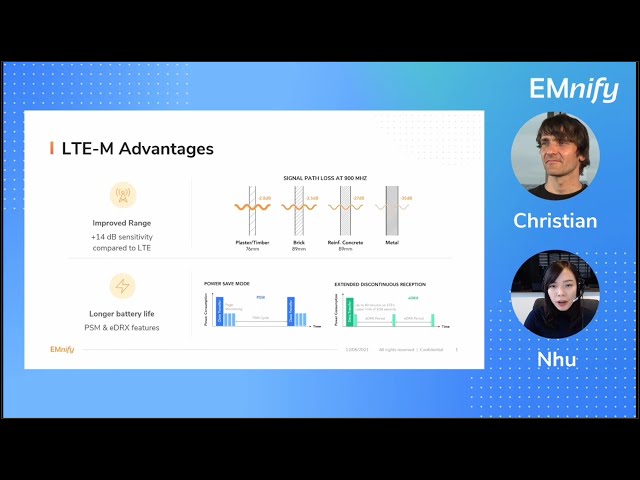
and refresher for the audience Nhu can you please talk a little bit about the benefits of LTE-M? [Nhu] yes sure so LTE-M is similar to NB-IoT the new 3gpp standard that falls into the low power wide area network technology so as with many other LPWAN technologies LTE-M provides two very attractive benefits for IoT devices and applications which are extended range and very high power efficiency. So extended range here means much better indoor and underground coverage so just looking at the comparison with LTE or 4g LTE-M provides actually 14 db higher sensitivity which means it can tolerate 14db higher signal loss compared to 4g and this allows the signal to better penetrate through newer construction materials like concrete walls or fire doors and enables successful message delivery even though the device are located deep inside the buildings or surrounded by a complex infrastructure for example. And as for their power consumption part LTE-M brings two new low power features which are power-saving mode and extended discontinuous reception so simply speaking these two PSM and eDRX features they allow the devices to basically fall into sleep mode or idle mode for an extended period of time so to save power consumption and enable a very long battery life. Another very important benefit of LTE-M is that compared to LTE the module price is much lower so basically the LTE-M module price is around one-third of 4g model price which also makes it very attractive alternative to 2g and 3g technologies which are quickly phased out worldwide at the moment so just a simple example of in North America you can see that the majority of network operators in Canada and USA have already stopped their 2g service so this is really an urgent matter and 4g LTE-M is forward compatible with 5g so this means that later on if the network operator decides to turn off 4g networks to free up their spectrum for 5g use then your devices can still stay connected and you don't have to replace the sim cards or go through all the hassle of certifying their devices so those are the key benefits of LTE-M for IoT application [Christian] thank you for the introduction hey one of the most asked questions in the community is how does LTE-M stack up against Narrowband IoT can you maybe share some insights there? [Nhu] Yes definitely it's a very common question given there are similarities between the two technologies but i would say both LTE-M and Nb-IoT have their own strengths and it's all about mapping their network criteria against your use case and wherein which criteria is more important for your IoT applications so let's start with ambition. So the main advantage of Nb-IoT against LTE-M is the relatively lower model cost however if you consider that both LTE-M and Nb-IoT are very new technologies and in most cases you will want to use a dual-module with both technologies and also 2g fall back to ensure consistent network service in multiple deployment regions and in that case then the device cost is basically the same because the module is then the same type of model.
the second advantage of NB-IoT against LTE-M is that it provides a slightly better range so if you look at their maximum coupling loss which means the total tolerable signal loss along the transmission path you can see that the maximum coupling loss of NB-IoT is slightly better than LTE-M which means that the signal can travel further and can also handle better the obstacles during the transmission path. however here you also need to consider that to enable the maximum range you will need the maximum transmission repetitions which then come at the cost of power consumption so that is NB-IoT. LTE-M definitely has its own perks as well which makes it very suitable for a wide range of use cases Where NB-IoT cannot cater to first very straightforward the maximum data rate of LTE-M is much higher than NB-IoT which then translates into much-reduced latency and also making it more suitable for medium bandwidth applications or applications where millisecond latency is kind of required also a very strong benefit of LTE-M is that it supports cell handover which makes the technology more relevant for more mobile use cases So cell handover basically means that a device can travel from one cell to another seamlessly without losing the connection so for NB-IoT because handovers are not supported this causes two problems. The first problems is that if the
device moves to a new cell then you will have a temporary disconnection period until the device attaches to the new cell tower and the second problem is that because without cell handover the device doesn't recognize that it is now traveling to a new cell area and is closer to the new cell so it will still try to connect to the old cell tower which is getting farther away until the connection is completely lost and this causes more power consumption because the farther the distance between the device and the cell tower the higher the power consumption it will raise the transmission power and also increase the repetitions and the last very important benefit of LTE-M is that LTE-M roaming can basically be enabled over legacy 4g. this kind of provide much better global and national roaming availability with LTE-M. For NB-IoT because the technology uses like the network operators they have a separate new commercial model for Nb-IoT. And this commercial model has yet to become mature in
roaming scenarios and that's why still the roaming is very limited for NB-IoT in roaming scenarios so those are basically the key differences i would say between the two technologies [Christian] one thing that I realized is that often our customers are using the LTE-M and narrowband IoT combined module because they want to roll out in North America where LTE-M is most dominant and also in Europe and Asia pacific where there's a mix of narrowband and LTE-M so considering that this these modules support both LTE-M and NB-Iot is there then a difference in power consumption when using a specific technology? [Nhu] yes so power usage is a little bit of a special case here because there is not an absolute winner or loser when you look at the power equation, there are a few factors you want to consider: so first the usage during transmission or active mode then the usage during idle and sleep mode - so basically psm and edrx cycles and the last one is the data rate which then decides the device transmission airtime. so what we mean with the last factor here is that the higher the data rate the faster a message can be delivered and then the faster the device can then switch off and fall into sleep mode to save power consumption so just look at a real-world example of one of the most common cellular LTE-M model which is the Quectel bg95 m3 module you can see here that according to their specification of this module the power or the current the trans the current power current of the device during the of the module during the PSM and eDRX cycles are almost the same between LTE-M and NB-IoT so there is no significant difference here for active mode NB-IoT definitely has a higher advantage here but then if you look at the maximum data rate you can see that LTE-M provides a greater much greater advantage here so the bottom line here is that if your device to send smaller message size which is around five-ten kilobytes then Nb-IoT is definitely more power efficient however the more data you send the more power efficient LTE-M gets so in a simple example of if you want to um send a firmware upgrade to your device um you then and the firmware upgrade is around two megabytes large then we end LTE-M it takes only 27 seconds for the firmware upgrade to be delivered while with NB-IoT it takes up to five and a half minutes which is a significant period and a lot of power will be consumed during this whole period um so yeah so basically it all depends on your use case and the amount of data you want to send [Christian] thanks Nhu I think this was a good introduction to the technology so if to the audience - if you have further questions please use the question panel to ask Nhu any question that you have around the technology. But Nhu now let's come to what the EMnify coverage looks like. So where can EMnify provide LTE-M service currently? [Nhu] yeah sure so with the EMnify IoT Sim besides the existing 2g3 g4g access that is currently already available now you can also have LTE-M access in 64 networks in 44 countries around the world. These numbers are constantly changing based on our latest internal tests and also updating agreement with our network partners as well - so you might want to regularly visit our website to check the changes in the numbers.
If you take a look at the map here you can already realize that the majority of LTE-M coverage is in North America and Europe with also some countries in South America Asia Africa and Oceania Very noticeable here also as well is that there are actually different level of coverage which then indicates a different level of insurance of the LTE-M service with the EMnify SIM. So you have the expected observed validated and guaranteed coverage. [Christian] Thanks i would like to ask that question because we want to be very transparent when we launch the LTE-M service: Nhu can you maybe give a little bit more insights about what does these different service levels mean? [Nhu] Yes definitely so as i shortly mentioned before LTE-M roaming can basically piggyback on 4g roaming because their technology is viewed as 4g technology and that's we as EMnify we expect that with our IoT sim our customers can actually connect their LTE-M devices in regions where we have 4g roaming agreements with our network partners and then the respective network partners they also already deploy LTE-M in their infrastructure and that's where this expected coverage comes from however as you can already somehow guess the expected coverage doesn't give an absolute guarantee that their service will be available there and that's why EMnify takes multiple approaches to basically give our customers a little bit more confidence and in the reliability of the LTE-M service so one of that is that we observe LTE-M devices managed on our platform to see whether there is LTE-M traffic for the respective network and that's where you have observed coverage here and then the next level of insurance is to really conduct internal tests for their expected and observed coverage to validate really the LTE-M service for the respective networks and finally the ultimate goal is to deliver really sustainable and reliable roaming agreements with our network partners so we basically already proposed them LTE-M roaming agreement with our network partners but some of them haven't yet dedicated roaming agreements yet. so everything is still under in progress but in the future we expect that we will continuously expand our coverage for our customers. [Christian] Thanks Nhu. so there's a question around this coverage map.
there are some more networks on this map than there is actually available on the GSMAwebsite and where LTE-M is proposed. how does that come in place? [Nhu] yes so basically network operators they are not obliged to inform gsma regarding their deployment or either is LTE-M deployment or the similar cases also with 2g and 3g phase out so most operators will inform GSMA regarding their deployment but not all of them actually do and that's why on gsma you will see you will find little less fewer networks compared to our coverage map and here we are at EMnify we work very closely with our network partners and that's why we get updated information directly from our network partners [Christian] thanks - now let's consider Nhu if we have a IoT device and you want to deploy globally what are the things that you should be aware of when you deploy the solution globally [Nhu] So when it comes to global deployment their first definitely their network availability which means then global and national programming so global running for to ensure that your devices can work in multiple countries where you want them to and natural programming here means then access to multiple network within one country to provide fare over and kind of more reliability in their LTE-M service for your device within one country the second very important factor is feature availability for example like PSM and eDRX especially if low power is one of the key driver in your LTE-M adoption um the third one then is the frequency band so what are the different bands currently used by their network the respective network operator in their respective countries and regions where you want to deploy your devices [Christian] Nhu based on your last slide there was one one question from the audience in North America does EMnify have LTE-M coverage on Verizon? [Nhu] on Verizon? so I don't have the information at the back of my head but we have the full list of LTE-M availability on our LTE-M page. So you can already see here in the slide that there is the link here where you can access the page to really find out what are the available networks that we have with LTE-M and also the specific coverage level for the specific network [Christian] If I recall correctly we do not have Verizon in North America we provide T-Mobile US and ATT - so you can even use two carriers in the US. [Nhu] So yeah I am checking in real-time, so in the USA we have ATT and T-Mobile as validated coverage and in Canada we have already roaming agreements with Bell for LTE-M coverage and also we have Roger Wireless as validated and Videotron as observed coverage For more information please visit the Website. Like all the information is in there [Christian] Cool I think that answered the question so let's go back to the previous slide because I had there a specific question around feature availability. PSM and eDRX you have pointed out how relevant these are if you want to deploy low power solutions PSM and eDRX are kind of mandatory from the GSMA deployment guide - so operators are supposed to make these features available Can you give a little bit of background how does this look in the real world if you use EMnify? [Nhu] Yes so if you are familiar with the GSMA deployment guide then you already know that PSM and eDRX are listed as minimum deployment requirements by GSMA however the reality is those network operators -because these are relatively new features - network operators have not really supported these two features and if they do they do not make these features available in roaming scenarios yet At EMnify we try to be as transparent as possible with our customers regarding the PSM and eDRX availability and we basically take two approaches similar to our coverage. So one is to validate
or to test and confirm the feature availability for the specific network the other is to ensure is that you have sustainable feature availability via roaming agreements so you can see here this is the full list of networks and countries and region where we have already validated and guaranteed PSM and eDRX available. SO maybe you also realized that this is not extensive yet but we are constantly working on with our network partners to ensure that you have increasing availability of these features in the future [Christian]: One question - about this global deployment if you look into how challenging it is to deploy global solutions with LTE because of the different frequency bands How does that look like for LTE-M? [Nhu] Yes - so for sure. The challenge with multiple frequency bands is still there with LTE-M because if you just take a simple example of the u-blox SARA-R400 series there are 11 different modules with similar functionality and service but support different frequency bands and therefore are relevant for different deployment regions the challenge here is that the modules do not support all the different frequency bands - so you want to look into the frequency bands that are really used in your deployment countries and regions and then choose the module accordingly Now here there is a tip from us. So as I said there are multiple frequency band generally available for LTE-M but actually in real world there is only a subset of bands widely adopted by the network operators and you can see here that on the left hand side this graphic shows the commonly used frequency bands per region this information you can doublecheck with the countries where you want to deploy - so you can minimize the device certification costs for the used frequency bands. [Christian]: Cool great session i think we we shared a lot of insights around LTE-M. I still want to give the audience the time to ask questions so if you have any
please please go ahead. Maybe one questions from my side - narrowband iot support how does that look like for EMnify? what's the story? [Nhu] yeah so i have also quickly mentioned before that Narrowband IoT use a different commercial model and that's why where the roaming challenge comes from so here at EMnify we are working on their basically their building and charging evolution process so this is the type a new type of building model for new technologies like NB-IoT and LTE-M as well and with that then we can enable roaming agreement with our network partners and provide um also in the future more more availability for our NB-IoT service so currently we have um in total around 13 networks where we have actually tested or validated uh or guaranteed coverage with NB-IoT but we expect that this will increase in the future as well. [Nhu] okay Nhu thanks a lot for these great insights, i think we are going to come to an end of this session and I just wanted to thank the audience for joining and Nhu for being such a great expert in this field just adjusting the camera here a little bit :-) yeah thank you for joining i hope this answered a lot of questions that you had around LTE-M you we are always available for other questions that you have if you want to get an answer also after this webinar you can just reach out to our support team or reach new and myself directly and we will be able to answer your question now i want to come to already the next webinar that we planned for that next week at the same time in the same position i will be here talking with our developer advocate Shruti Kuber around our announcement of the Cloud Connect which we have now made available in 20 AWS regions so basically worldwide you can directly peer with your AWS deployment because this is quite a technical topic i'm really happy that Shruti will be joining me and will also do a short demo around this and will be able to explain the benefits and how this is deployed in your solution so if you're interested to learn more you can basically go to our website and register for the webinar and of course as always you will get the recording of this webinar and some further information afterwards. one more thing before before we'll close this webinar
when you close the webinar there will be a short survey around what future topics you would be interested in or which partners you want to have invited you know that we had for example AWS STmicro or Saft batteries here and i would like to know who are your partners you're working with and who would you like to talk about their solution in this webinar series and with that i would say goodbye thanks for thanks for joining and see you later bye you
2021-05-23