CIS40A Unit 10 Lecture: Wireless Technologies and Network
okay we'll go ahead and get started so this week we're going to talk about wireless networks um I'm sure that we have covered tidbits of details from before and you probably learned some of the encryption information from another class but today we'll talk a little bit more about Network Technologies and wireless um requirements for setting up wireless networks and then later on we're going to do a lab for um with server which we talked about last week like DNS um so you will need a drive for the next part or the second half of the class okay so let's let's go through Unit 10 um and also I had sent you test out access code make sure you check your email um you can use that code to activate so you just click on the assignment and then it's going to prompt you to um the homepage of testout and then you can follow the step describe on the email but make sure that you keep that information in case you need it later on uh you do have the license for a year so you can have access to it later if you need to come back to study for the exam or do some of the labs you're welcome to use all the resources in test out U for this class I'm only requiring test out for practice exam and that's part of your grade so we'll we'll come back to this topic later okay so the first uh page of the notes include information about Wireless technology we know it uses radio frequency um and the signals is transmitted over the air um what you see is radio wave signal so that means that the farther you are from the source right you know that you would have less signal as most of you are familiar with your your mobile phone or your smart devices and so what we want to do is we want to think about the technology when you set up wireless network everybody has a wireless network right and we'll talk about the integration of wireless network in the larger land your local area network so um so with that we should be able to answer question number one it says explain the relationship between frequency and distance in the wireless networks so when you have a frequency right that means that if you're using 5G that will be transmitted in the shorter Span in distance so when you're integrating 5G wirel Network [Music] local your devic are only going to be able to pick it up in a shorter different right so meaning that if you have a device that's really far away from the source you will likely not be able to connect to the actual uh 5G access point when you using lower frequency which is at 2.4 gahz for wireless the signal is transmitted in a larger or longer distance so there is an indirect relationship between frequency and distance and you also need to know that there are uh things that will in signals such as glass water metal right this is why when you have your wireless router at home it you know from between the wall sometime it's not able to pick it up so if you have a metal plate inside the wall that's going to also bounce your signal the majority of your wireless devices right as you can say for example your smart TV um even your wearable devices those often operate on 2.4 gahz and that is your average um integration with Mo with wireless devices but you would have the Dual Band devices that will be 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz right for the AC and the ad um that's the new the new um standards for the i e Wireless so if you need to integrate Wireless devic in a larger distance we want to consider right we want to consider lower frequency 2.4 gigahertz compared to you can have faster speed right higher frequency higher frequency is going to give you higher throughput but that will be closer in proximity so that means that if you have a building right you can integrate yes you can use 5G depending on how large of the building how far away from the access point that you're using so we have to really be able to kind of scale out our signal when we're planning for wireless network okay hi okay so that would be the first question and you can find some of this information on the first part here I just summarize it the second part of this it talks about antennas and antennas is important sometime we want to use omnidirectional antenna that's going to pick up signal all around 360° sometimes we want it directional uh for example you might have a building like in the hospital um you don't want a certain Wireless signal to be passing through a certain part of the hospital um section where you might be running MRI devices um or things that might have conflict in in Signal um so you want to aim the antenna in a certain direction where it would be suitable so sometime we would have directional antenna and sometime we would use omnidirectional and often that we would have omnidirectional where it can pick up signal all around right or it sends signal all around um but then we can intentionally set up a directional antenna so we should talk about a little bit about bands and ISM bands and how it's used so what we would see is that we sometimes would have frequency or interference in Signal um where you would have radio frequency that cross um you see this a lot um sometime you listen to the radio and then sometime you have a little bit of cross Channel I think we're doing a little bit better with some of the Bands um but in facilities like you would see office building you would have ISM band being used Healthcare facilities like hospital or healthcare provider places you would see that warehouses uh shipping and receiving or manufacturing warehouses and even homes so we would see that ism is actually being used everywhere right um we would be able to send and transmit or receive signal in the case that we would see radio frequency and also Wireless being integrated everywhere okay so here um it lists all the agency that's managing the standards Wi-Fi Alliance basically tests the wireless devices that you see when you buy wireless devices it doesn't necessarily have to go through certification with Wi-Fi Alliance the ones that do it just validate that they are you know meeting the requirements and normally companies would pay extra resource to be able to get it tested and certified um and then you have you know Federal Communication commissions who manages the wireless devices for United States and so when you are let's say that you're trying to build a Jammer right um to cause some kind of signal Jam for wireless that's considered a crime um the FCC can uh prosecute you and be able to uh go through the legal processes and you will be in jail for a long time uh so we we want to make sure and will you be able to buy Jammers professionally by companies that creates where you would have you know they would have like boundary protections for stadiums um you know things like that yes you can you can find uh organization that provides that right so they regulate the use of wireless devices how we manufacture wireless devices and how we use it in United States and then I just maintain the standards right I think we're moving from AC to ad um very soon because I think that because the encryption and everything else is a little bit better um for the new standard okay all right so FCC um we want to we want to learn that there are unlicensed bands that's used so often you would see 900 mahz 2.4 GHz and 5 gigahertz so you
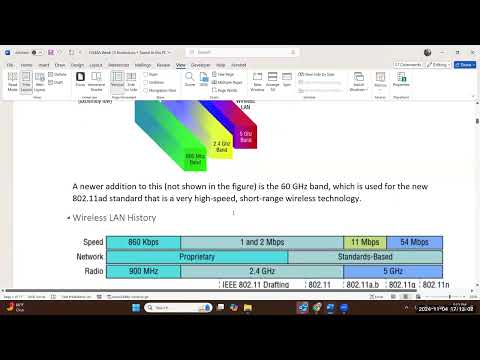
most of you are familiar with this the Dual Band this is what you have at home with your AC router uh your wireless router and then if you're using older devices you would see that it operates at 900 MHz which is a lot slower than what you see here right okay so if you are curious what ISM means it's industrial scientific medical bands that's used in like we said Hospital office building or even home right okay so here gives you a little bit of like an image on how the spectrum of your radio frequency uh breakdown so sonar is very low this is you know if you're familiar with sonar like submarine or even on boats or ships they use that for fishing boats to be able to map out the fishes right uh sonar signal is is low and then you got the FM broadcast this is your rad radio your public radio that you listen to in your car and then the cellular area is a little bit under 900 megahertz so you're at 840 and then from there in between from here to the visible light what you see here with the spectrum is your 900 band 2.4 and 5 gahz so we operate Wireless right here okay will we be able to exceed 5G uh down the line technology will allow us right but I think right now we're pretty new to the 5G area as as far as consumer integration I think this been around for a long time Wireless technology been around for a long time it's just for Consumer integration that's widely used across the world um is somewhat new in the 5G area Okay so that this kind of give you the historical right I think 5G been around since the early 2000 or even in the 90s I think it's just widely adopted now like I said okay any question we're not very full today all right so let's talk about the cellular network um that uses 5G I think that we some of us are using some of the former uh you know I think the integration for LTE and upgrade to that to the the the newer right this is what you see with cmob and then also Verizon um for the type of cellular network work that you see with 5G is your code division multile access your CDMA this is what you see with the older uh integration from 5G with Verizon network and some of the other networks so basically it it gives out a code for each of the call that's transmitted and then the data is kind of spread across the Spectrum allowing it to use various um uh frequency in the bank and then for your LTE this is the older technology for what you see with AT&T and T-Mobile um this is a standard Broadband communication for mobile and wireless device and it uses data terminal and it's based on your TSM Edge NS um Technologies so when you upgrade it from one technology to the next you have to continue that with the f G right um so this is why before when they're saying who's your carrier right if you have Horizon you have to sign Horizon because their mobile devices are built specifically to receive a certain communication uh type where if you are your carrier if your service provider is AT&T or T-Mobile you're able to do that and you still see that now when you're purchasing your your phone let's say an Apple phone um it asks you from an Apple website what which service provider are you using it with and then when you're using the one that is not tied to any service provider those are a it's able to work with multiple type of network so it's not limited to certain type of communication that's what you see with the 5G now you know that 5G is not everywhere in the world or even in the nation right there are some spots that don't have 5G even though there's advertisement for our service provider that 5G is widely mostly everywhere but in the rural area there's not even fiber connection so you will not have mobile Tower or or Cellular Tower that's being able to support the signal um so you do see that we we still have a lot of like rural area that we haven't developed out in communication and other part of the world is still using 4G or even below that right um so we are fortunate to have a higher frequency to use so that way you are able to have more throughput or ultimately faster performance in communication but it's it's inconsistent right it's not the same everywhere in the nation or even the world okay so for quiz and final exam make sure that you understand the difference between these two code division requires a code and and then for your LTE it is an upgrade from GSM or Edge right if you have um or if your parents use the older mobile device when you turn it on you would see this logo at the top right GSM or Edge and it is an upgrade to the LTE and then eventually transition so uh you know when you turn on the type up Network and then when you go to another country if you're using your mobile devices and connecting to their Network it will say the type of mobile network that you're connecting to right and that really breaks down to how communication is transmitted across okay wirelessly any question okay so for this type of information you can defer to the notes and it gives you additional information like if you're using a Sim that's formally based on gsm and then your fdma a for the frequency division multiple axis I know if you're studying for A+ you have to kind of know this too along with network plus right and then it gives you the tdma CDMA and LTE then now what we're going to do is we're going to go through some of the 80211 standards and here this table gives you all the standards that I E govern um do do we necessarily use all of them no right sometime you don't even see these make it to the consumer Market but it doesn't mean that it hasn't been tested or gone through the standardization so like for example like for Japan and US public safety there's a j we probably haven't seen that ever right you are familiar with maybe your area is probably AC or even maybe uh 80211 n right which is an old the technology this was very popular I want to say about 15 years ago for uh wireless network and then we upgraded to the AC a been around for a long time right and then b g and N those are the popular one for the consumer Wireless but it gives you some general description of the each of the standard so the wireless standard that transfer at 11 megabit per second which it's comparably to today's technology very slow but it was widely adopted um so wireless networks was something of maybe a preference and also like more more of like a extra to the network right so in the 8021 B era um want to say like in the 90s and it was used toward the end of the 90s and early 2000 B was not high in transfer rate um however the the the encryption at the time the technology that came with B was better than a even though a is going to give you a higher frequency B um but a21 be only trans transer at 11 megabit per second but for its time that's amazing because people were still using dialup modem right um or even maybe if they have cable cable was transferring at half of that or even maybe at the max 10 megabit per second so if they have DSL that's roughly between 5 to 20 megabit per second um depending on the type of DSL that they were using so Wireless technology for the integration 11 megabit per second for a lot of the business was amazing right and at the time you don't see a lot of the wireless network people would just you know they didn't they didn't have a lot of the technology to accommodate it and then you know they might have workers that have laptops or pdas which is what you see as transition to the smartphone that you have now um but the be transfer was fast for its time then we have an upgrade from the B to 80211 G and you see a tremendous jump in the rate of transfer right your throughput about it's it it multiplied by five basically so we went from 11 megabit per second to 80211 G which is 54 megabit per second and the encryption for the wireless standard can also o change okay you went from a we to WPA and now we know that WPA is very vulnerable to attack however at the time it was decent for for what it was right so G um was have some backward capability and it works with B so if I have let's say some old laptops that use 802 111b right I can upgrade my wireless router to G and it's able to be able to communicate with my laptop so back then the consideration is when you upgrade your wireless technology you got to make sure that it's compatible but if I have my laptops were 80211 a and my router is 80211 G that will not work right so you would see that there's some backwards capability um with the B and the g or I mean the G to the B um so if you have the so the fastest my laptop is going to be able to receive data is 11 megabit per second even though my router is going to transfer at 54 megabit per second so you would have slower devices but faster network connection and so a lot of the administrator would then upgrade the access point or the wireless router to the the newer standard as long is compatible to the older standard okay so we need to know about the channels I think uh during the first week we kind of touch on this so in United States we have 11 channels that are configurable and whenever that you go into the administrative page of your wireless router if you select the channel and if you click the drop down menu you're going to see these Channel A lot of the time your wireless router would have Auto config on it right it's going to select the channel That would be best right uh or default to Auto config so there are elabor channels that are configurable because they are overlapping in 2.4 GHz frequency this is on the 2G B right they are one six uh I'm sorry one six and 11 are non overl that means that you have channel two through 5 7 through 10 12 through 16 are overlapping in exception for 1 six and 11 why is this important well sometimes when you want to use certain things at a certain channel so that way there's not uh overlapping signal right um so I don't know if your home still has this I think most people don't have landline anymore but if your parents or your grandparents or someone you know might have a cordless phone and you would ask me what is that right it's a phone that has a little antenna and then you use it to call the landline right cordless phone operates at 900 mahz right and on the cordless phone sometime you would have cross talk meaning that sometime you might hear a leak of signal into someone else conversation or you know it's because the technology was not perfect back then then you have to select the proper channel on the portless phone to make sure that there's no leakage in the signal when you don't have a cross top right um so in in similar to that that example what you see is sometime you want to set up something that that's distant and that is not overlapping for example I might have one one part of the network that's going to use channel one and I don't want overlapping signal for another part of my wireless network so I would set up the access point for the second part with Channel 11 so you would have a farther Gap in that you don't have the overlapping but if you're looking at the other channels 2 to 5 7 to 10 and and 12 through 16 they are all overlapping um and then if this is only on the 2.4 gahz but when you're looking at the 5 gigahertz uh frequency right they have a longer list of the channel that you can configure or usually it Auto Select that for you on your device right but you you can definitely set up a specific uh channel that you want to use for your wireless network and so so why why would we do that right um it is for monitoring purposes it is for troubleshooting purposes it is so that way you don't have cross in Signal U and so there are multiple purposes in how we would set up S uh channels in in our frequency okay so um for the 2.4 GHz here it breaks down some of your standard like what we talked about right and it it it touches on the CSA CS maaca this is important you might you will likely see this on the network plus certification and so this is to avoid Collision so there is acknowledgement so that way you don't have Collision in in how your packets or your data is being transmitted and then here's the channels that we refer to so when we say 2.4 it's not exactly 2.4 right you know that it is
approximate so you would have like a little bit over close to 2.5 almost for the frequency so if you're looking at channel one it is earlier on in the frequency and then there's the six and then there's the 11 so if I use channel one and 11 it is farther apart so you don't have any kind of overlapping here is your 5G so your channel Center is a little bit different but it does break down in the frequency when you look at it yeah you got 36 40 44 48 and so on so the number uh for the operating Channel is a little bit higher than what you see in the 2 than the 2.4 and then there there is like basically a division on how each channel is operating so between like 2.18 to two five uh 5.18 to to 5.2 you see that there's 36 and 40 so if I'm using the middle band I would be up here right that's a higher Channel or if I'm using so this is ideal for outdoor so if let's say that you uh you often you want to set up something for your backyard and you have a very large area um like some people have Woods in the back or they might have like a little a you know guest home in the back and they they would put some kind of Wireless um or sometime that I might need to have surveillance camera of my property and I might have like four or five acre um and you can see that here too like in Hemet or some of the rural area so when you're using the upper band that's ideal for outdoor right and then if you're using both like indoor and outdoor like you know you might have a a smaller patio area and then also inside so that will be ideal um for the middle Channel and then your lower band is mostly just going so now we know when you look at your wireless router now you can see like I said it's autoc configured but but you know you can look at the channel That it selects there some TPC information and then for mimo for multiple input and multiple output so that allows you to have transmitters and receiver and T so you can have higher throughput so whenever that you buy devices and you see mimo m i m o right we just know that it is going to give us higher throughput because it has transmitters that's built in and receivers through the antennas so for seven it tells you Teresa configures an access point to use channel one in the building if she needs to another access point in the same building what channel you can use in the i e 821g standards in the 2 I should say this is under the 2.4 GHz right so if if she's using channel one already for one access point in the building we don't want an overlapping for the access point so we need to use a Channel 11 because it is the farthest it's at the end almost right to prevent overlap so when you have multiple access point in the same building if for the 2.4 GHz and
the same thing with the 5G you want to use looking at the indoor for the 5 you want it to have a little Gap so that way you don't have an overlapping in signal and that's just a them okay so when it's overlapping you you will have some performance issue right it will not be able for example like people are trying to connect to your access point and it's not picking it up um even though it's there and it's power on and other devices sees it um sometimes when you have overlapping like that um it's causing some issues in communicating and transmitting or receiving yeah you can but it's close so because let's say that my my building is 100 square meters um that is actually a close proximity a lot of times when we when we add in devices you run the devices to the cable all of these Wireless uh router access point is still connected to co axle or likely ethernet cable and so you limit it to 100 met uh 120 but 100 meter for Ethernet cable so if I use Channel 6 there is a small chance that it is overlapping but yes you can use a channel for the two 2.4 GHz so it's recommended ideal situation is that you want to be a little bit further out okay let's move this down okay um so in the section where it talks about it talks about after the channel and and right before the mimo section it goes over your Dynamic frequency selection which is known as your DFS in the BL you in the wiress network so why do we what why do we have to have a device that has this particular feature this feature is important it prevent interference that occurs across the wireless network with devices right um and you don't want interference interference in Signal deplete signal so that means that when you have signals that are o you know on top of another signal or causing conflict with um what will happen is it would increase in throughput or ultimately cost interference so that way there's H there's no communication right um and you can you can see like you sometime you can hear interference right when people have smartphone in their pocket and they walk toward a microphone normally you would hear a pitch right on the microphone because at that point your smart devices or your wireless devices sends out signal through the airway and also the microphone is receiving some signal instead of your own voice or your sound it received that signal so that way it is being carried and heard on the speaker right so what you see is you do see some interference we have interference everywhere we just don't acknowledge it right when you have cables together you're going to have leakage in Signal um and and when you have a lot of that you are going to have some either delay or slow down or deplete in in performance so you want to make sure that you have quality of service all the way around for your Network Technology and then in that same section it talks about TC TPC which is transmit power control in the wireless network this allows the client and the AP to communicate with left power this is important for when you're looking at things that are industrial um for example you drive around downtown Riverside if you look up near some signal light area or the light you know near the light pool you might see little solar panel um and I know that you know Marino Valley is going to start integrating that um city of lomalinda has it there are many city that operates mostly on the wireless network um and you want things that consume less power to be able to maintain the the the devices so that way energy consumption is not a big deal so it it would what it would do is it would have preservation mode on these um devices so when it's not fully in use it would have an idle mode or like a preservation mode like I said to reduce uh power consumption but on top of that the battery power power it has the interference reduction and it would use less so that way you don't have a lot of the interference with other right W land or Wireless uh technologies that are in surrounding the neighbors So when you buy wireless access point or router you want these two things right they are beneficial for your device you want to get something that has TCP which reduces power use um it has to preservation for power and it has less interference with the neighbor wireless devices and you want to have the fs your Dynamic frequency selection so it's able to Auto Select or change um use various frequency asset needs because remember your frequency is tied to channel right so autoc configurable options are ideal and then we touch a little bit on mimo so mimo um multiple input multiple output m o this is using multiple transmitter and receiver antennas to increase data through put so you also want this particular feature on your wireless device now some devices doesn't have a physical antenna that is attached to it um like you see a lot of that like your smart watches it has you know antenna that's built in it's able to detect other right like your wireless routers and things like that um you might your smartphone doesn't have an antenna that's attached to it that will be tacky looking right that's like the old cellular phone that you would see back in the day but it does have the integration of the chip that would have the sensor to be able to pick that up so um and then if you're looking at wireless routers or access point those have physical antenna that's attached and you want to have Nemo okay so let's put this up a little so we can see the bottom okay sis1 Carlos bought a new wireless router and found Wi-Fi sticker on the box what does the sticker in five so whenever that you see the Y Wi-Fi sticker on on the device um on the box basically that has been through the certification and testing process with Wi-Fi Alliance that means that it is interoperable right that is tested across multiple types of devices um and basically you don't have to add the second part but it is they want to ensure that all of these things are Backward Compatible so I think on the AC now they are Backward Compatible with the earlier standards so what you would have is if you see the Wi-Fi sticker it just mean that they have backward compatibility and interoperable across multiple type of wireless devices do you have to have something that is uh Wi-Fi Alliance tested no right there are devices that sell are sold a little cheaper but they haven't been through the test um manufacturer will produce and be able to push them out a lot quicker because the testing process costs and it it takes up time so sometime you don't have it certified but that's okay it's still it's still capable of doing whatever that it's supposed to do so you see this with older technology also okay so for the AC right we transfer at one gig so one gigabit per second for the AC more or less so someone might ask you since you're taking networking class which one is faster ethernet cable or Wireless what do you say ethernet definitely 100% 1,000% right ethernet interet cable is going to be faster and wireless you know you have to consider other Factor too right line to side blush you um Additionally you also have things like you would you would have to consider if there's other things that might impede your signal um in between from your access point to your device I think in a couple years from now right AC will probably be old technology uh people still continue to use it until the new technology fully integrate so I remember when AC first came out everybody wants AC and wireless router that or AC were very expensive because everybody wants to be on 5G um so expensive any question okay for 13 Paulo wants to upgrade her wireless network speed she purchased the new 80211 AC wireless router in her home network she is using two laptops that that have 80211 and wireless adapters um what is Paula system maximum transfer rate how can she improve the transfer speed of her wireless network right so she has a new router and we just learned that AC transfer at one gigabit per second but she has some old laptops that uses 80211 n which is the technology right before AC so her laptop would only be transfer ing um approximately 300 megabit per second up to 450 half of the AC rate with an antenna if if it using an antenna then it is a little faster than without the antenna so to really upgrade the network transfer rate we would then consider upgrading the laptop wireless adapter so what's your recommendation we don't want to open up the laptop and and install it right that is okay USB AC wireless adapter is ideal and it's less than $10 so she can buy two as long as this her laptop uses USB 2.0 and above uh likely that it is 2.0 right we can install the driver or it automatically loads the default if it's Microsoft Windows PC then it loads that so for $20 we can get her you know a little bit faster speed on the laptop and it will be transferring close to what we intend for it to be which is the AC rate right so when you work at Best Buy leak Squad you have to give them advices like this on how you can improve but when you work as an it consultant sometime you have to do that you have to say Okay well you have some old technology let's make it work instead of replacing the laptop which is expensive right the idea is to get the network performance as fast as we can for the very little amount of money so USB AC adapter will do the trick okay at most $3 $40 but for both but usually they're like about 10 bucks each any question okay so here it talks a little bit about spatial multiplexing we already learned about multiplexing in the past it does have that capability to optimize for multiple path resistance and then you can also have Channel bonding that means that you can group the channels um and then we we normally filter Mac addresses and then using the proper protocol uh with your wireless technology here gives you a little bit of the layout on the rate for each of the standards starting St in with a G and B it doesn't have the end like what we touch on and then also the distance I think most of the networks now is with AC but you never know you might run across an older Network a backup Network maybe um and in the security world that's a flaw right whenever that you're using old technology and you're not updating uh like encryption and things like that we look at that as an issue so we have to close the gap on that so we we either advise them to upgrade um or like you know reduce the use of of the system okay so antenna information and then a little bit on the yagi right um this is point too antenna um a similar technology I'm sure that some of you know this right if you drive around the neighborhood people might still have antenna on their roof um and that is a point to point so that way they can pick up local television channels and things like that um it is power in a single Direction so back in the day a lot of people used yagi um you know you have to angle your antenna a certain way to receive your signal a certain way so it is directional um but you know people you can also build it too there are tutorial on how to build that okay let's see sorry let's switch over to the next part okay for 14 is this Max's office is 200 feet from the company access point it is an older access point 80211 G why is Max laptop transfer rate at 11 or at 50 megabit per second much lower than the transfer rate of the speed so G transfer at 54 megabit per second right so we're only doing like a quarter of the transfer rate uh so he is 200 feet his office is 200 feet from the access point and we can see already that is just a distance so the dgr in of the signal is caused in the longer distance so when you are over 100 ft what do we do we need a repeater okay um maybe adding another access point in the office for the people at the end like Max's office or you need to have a repeater and even if you have a router or an access point with a repeater built in the repeater or an amplif fire just take that right the repeater takes the signal and repeat it amplifier takes the signal and increase it so the frequency is volumized so people tend to make the mistake of lumping those two into one a repeater take the signal so if I have signal a that signal is being being retransmitted an amplifier take the signal and volumize it so it's like listening to the radio in a higher volume that's an amplifier right for the signal but in a repeater when you're listening to a radio at a certain sound take that sound and relay it down the line so that's different okay for 15 it says in a wireless network what type of device is connecting all the components together which is we all know this right your access point or your wireless access point your WAP now your router at home your wireless router it acts as both it acts as a router and an access point okay so an access point connected the components together your smartphone your PC your game console your smart TV all of those things your router brings internet into the home okay because people tells me oh my access point gives me internet no your wireless router gives you internet your access point connects all your devices together as a network your home network okay your router is both of those it t it takes on two roles it routes and it is is an access point okay but in a larger Network like here rccd or when you go to a business an access point is just that okay so that means that I have I might have 20 access point across let's say UC Berkley right or UCR or cowall and pona for the students and it's all connected back to a switch that is connected to their main router in the in the network and that router routs out information not the access point route in and out okay can I have a wireless router in that Network sure and we can segment it on of a VLAN specifically for that but your backbone should be Central Iz and it manages all your wired Network and your wireless network so your wireless network is going to come from like maybe a VLAN or a segmented network but it all of that is going to funnel back why we need to monitor all of that so if someone is attacking my wireless network I can see it right but if you you can have a bunch of routers but all of those router need to talk to some kind of appliance that monitor those and then the antenna that's used on the access point okay the antenna that is used on the access point is going to be your Omni antenna it's all Direction 360° now we might have certain cases where we only need a certain direction so for example you might have um a a wireless segment for maybe visitors at the hospital and it will be for that section only but the other you know the others we don't so you can use the directional antenna in certain cases okay pretty easy question and then on the next question it asks you what type of antenna is used to connect two access point together right you got two AP that needs to be connected you can use a yagi they are directional and then in the next part of the notes right at the page where I stop it talks about an ad hoc network and how you can install an ad hoc network we use it all the time I think that we don't pay attention to the terminology or we don't know what it is so whenever that you using like a peer-to-peer Network it's also consider an ad hoc network so two computers connecting wirelessly using the wireless adapter like I'm connecting my laptop to my other laptop right but so how do we specify that it is an ad hoc network well when you install your wireless adapter and configure your wireless adapter like or you know like how you go into your uh in the PC it refers so when you go into the properties of your wiress adapter you can specify that it is an ad hoc setting so where can I find this information in my notes you can find this on page nine just know that the the key here is this is IB S I know CompTIA A+ books also include this information but it's known as independent basis service set okay when you have two devices that are wirelessly communicated this is established ibss so and a lot of times we are defined by by proximity of the devices when they're communicating with each other right and then when you're using basic service set which is just BSS and this is infrastructure mode so when I use an infrastructure mode what does that mean when you come to rccd MVC Norco CD college and you connect to their wireless network like I am right now that is BSS right we are connecting through an access point when you go home and you connect to your access point so that way you can access like your wireless printer to print out your assignments or whatnot right that is is your infrastructure mode your basic area service set so for 19 it says Mark is installing wireless network for a small business consists of an access point a small business server laptops wireless printers what type of wireless network is Mark and soling and that is your BSS or your basic right uh so that will be your infrastructure mode okay compared to ad hoc network so ad hoc network is when we're connecting device to device where infrastructure mode we're connecting to through a centralized point it becomes a star topology so you are centralized by the access point to all the other wireless device so to assure that the user is able to access Wireless signal what is the recommendation for installing multiple access points inside a network so if you have users across the entire campus right when we're looking at like a college campus or a University campus or even a a large company with different sections of the facility you will have many access point we don't want overlapping Channel don't get this wrong right it is overlapping in the signal meaning that the circumference of the signal should be overlapping with at least 10% so how do I be able to set that up so what I would do is I would start from one wall right and I would get a signal reader AKA your smartphone works just fine right but we we have T devices like that we would walk toward the edge of that circumference the end of that maybe that building or that room and we would read the signal okay so when you get from a five bar to a one bar that's at the edge but you want to overlap before the one bar you want at least 10% normally I prefer 20% so that way when someone stands in that spot right at that edge they still get signal but it's going to be enough right not low where they cannot transmit anything so and then you would do that so your circumference for the signal you want that overlapping by 10% not the channel okay but so your access point should be like that so where do I mount the access point right before the edge of my signal where my signal end right so if you look they have an access point right around here so you get some signal in the parking lot and then when you go over to the other side where all the main buildings are there are multiple access point there so they need to be able to determine that so when you installing the wireless network as a technician or even engineering you manage this right let's say that your company is expanding right they're building another area maybe for manufacturing for the robots to be able to you know build and create and you know manufacture things and you need to have access point out there because they might have wireless devices or and the robots are mostly all Wireless in communication uh as they are iot devices so you have to set that up I think I have a picture for it okay so this is what you would see in a in a distributed environment right we talked about that earlier this is what I'm talking about here so 20% so from one access point to another access point we need to be a little bit overlapping so if someone is using their devices here they still get a little bit of signal right but normally we want to plan this and engineer this so that way no one should be at the edge like nobody's office should be right there if it is you got to move their office because you're going to get you're going to get troubleshoot ticket all the time about network issues okay so you want them to be and you would you would build that out right as many of the access point and ultimately it connects back to your main switch and your main router so when we say land backbone that's your rack where your router your switches your Uplink switches are connected so your access point still is cable connected to those so how do they do that in the city what do you think if you drive around you look up oh there's an access point so that way when someone is you know in that area in the Civic Center when they're going to court when the lawyers are walking their way there they can still connect to that I I like using public Wi-Fi but who knows right they can still connect to that City so how do they do that it's still going to be underground or through on top right connection you still see it right it might be power with solar but you still have to connect it back to the network regardless if it is wireless connected it's relay to back to the network so that way the city Network actually manages all the device right you see that in a lot of like the the smart uh City now I think like things like people are building out part of Chicago or even uh some part of the world like in Malaysia and so on um almost all their devices are wireless and you still have industrial routers and things access point that uh relay signal back and forth okay so you still need to connect it back like this so you have a a a wireless controller an appliance that's going to manage all of them right I normally segment this so that way it is not all inside my network because someone it's so easy to get into the wireless network right you already know okay and so if they can get to your wireless network they can get to your network so that the whole point is to make sure that you segment it and then there's proper configuration with the security Appliance so that way it detects and you know normally they throw this on a VLAN and then segment that with because it's uh you can route it in so you can just use subnet to be able to manage it okay um let's do some of the last part try to give you some time to do DNS today okay so for 21 it says what is the main difference between a wireless Standalone and a control based wireless network and you can see from that picture that I just looked at how are they configured so first the Standalone controller doesn't require a full OS they are managed independently or individually managed second the control sorry the control BAS system has full operating system the controller is configured to manage the other ACC whether it is a server that you want to manage a lot of the times we use an appliance and an appliance would have some kind of operating system including your network Appliance so uh some of you were using the switch successfully and some of you were using the switch not successfully because the models are different but whenever you you boot to those Appliance you can see that is an operating system that you're using and you might be controlling it with the commands or you might be using graphical user interface when you click right so there there are operating systems are integrated so in the control based system it requires operating system and operating system is just a software tool that we use to uh to be able to control the hardware device right for humans to interact and manage the hardware device so in the control based environment you have to have the OS whether you using like a server OS an appliance OS some form of os where the Standalone controller doesn't require that basically it is individually managed some autonomous system it is individually managed so that means that it doesn't require the full OS function it's just going to execute the function that it's written or coded to do right receive signal right store and data retransmit signal and that's it right that's a very simple function to code compared to the the control base system where you have to have more complex requirement in how you manage the other devices so when we when we look at wireless network design these are the things that you you need to consider distance first right it is line to sight so that means that we how we how far we are from the source is important walls whether it's Rick or metal walls or in California we might have not well insulated walls or in well insulated walls walls will bounce signal right remember what I mentioned to you you before right when you using access point or uh even cabling when we go from one floor to the next floor we use Fiber when you have one floor to the next floor use a separate AP we don't integrate AP because there's no way it's going to go through the floor right you already know that at home it might work that you have your router upstairs and if you're in the living room downstairs you might still be able to pick that up but it doesn't work like that in in business facilities so we integrate different access point for different floors and sometime multiple access point for the same floor depending on how large we're looking at and you run the cable through Elevator Shaft right so and then sub ceiling and subfloor to to hide all of that we also need to consider protocol limitations right with wireless technology and the standards that we use so it's very important that you consider that the aspect of this is the encryption encryption is about your key Lane right um because you know the the the simple the more simple the key the easier it is for them so basically security just means buying time so protocol limitations um interference with other devices so when you work in facility that might have other devices that generate radio frequency we have to consider that right or other wireless devices that has its own signal so we have to consider that there will be some cross interference okay and then I'll come back to the notes once we get some of this knocked out and then before installing your wireless network when you what should you do with when you do site serving so earlier when I mentioned that you need a signal reader right and then looking at how where you going to mount how you going to mount how you going to run the cable how you going to generate power right all of this is part of your your plan when you're trying to engineer or expand your network with the wireless network so we need to consider the scope of your network okay meaning that what are you really what is your wireless network intention right how how much accommodation for your wireless devices how many wireless devices are you trying to accommodate right let's say that I have a thousand people or maybe a very small place like you know those coffee shop or restaurant see so you have to look at the scope of your network the type of Dev that are going to be joining your wireless network right um whether it's most of the time it's going to be your smart your your smart and mobile devices so your laptops your tablets your handheld devices and so on and their compatibility you need to make sure that you have expected bang withd capacity and this is important all the way around right we don't want you know if if if let's say you H you you have the restaurant and all of a sudden it became a very popular restaurant because somebody had put it on social media and then you have a lot of people there so if you don't have the the performance capability and scale what will happen is your your network is just going to be depleted then somebody writes a bad review and then your restaurant will go down again right so when you're looking at that from a business perspective we always want to think about performance Capa capacity and accommodation for our Network right because ultimately it is service and it is business okay so here earlier we talked about these barriers and Signal degreg um signal loss right in in depending on some of these factors and then um these are some of the things that you want to consider for Internet of Things So Internet of Things Beyond just your Bluetooth and wireless it uses other things like zwave that's for home automation or this is also known as zigby right um your ant plus this is a different protocol for sensor monitoring like um you know if you have like pressure sensor or indoor lighting uh that kind of stuff smart bulbs um if it's not using Bluetooth and it's using ant plus and then your Bluetooth technology Nei communication we all know right most of you if you pay with your ATM card or credit card when you do a tap that's NFC uh with the chip and then infrared uh RFID this is for a lot of time stores use this for loss tracking right in those um UPC tags and then there's a whole section on how you can configure right beaconing the SSID or not um I recommend Mac filter on on wireless uh networks that's crucial right so that way not everybody can connect and then you can also um use firewall features to be a ble to block port and service so this is a screenshot I think every book uses the the links this because they're just popular which is owned by Cisco right but your router would look similar but not exactly the same so how do we get access to this right the default IP address for your router you put it into your browser and it's going to open up the login page uh with the right username and password you should be able to access the configuration mode or the administrative mode of the the wireless router that you have at home and then you can go through the setup and the Security Options sometime you would see the vertical tabs or the horizontal tab similar to this and then site survey information this is purely for Gathering information and this could be for uh you know building out planning right or even re-engineer part of that Network so you would do this they call it predeployment that means before you make it active and live and be used and then you also do it post deployment when you get rid of it okay so let's say that I'm sorry not get rid of it after you have implemented it so we want to make sure that everything is good to go and capacity remember what we talked about 20% overlapping it should be like this okay our cross I mean in a box like this that's easy to to kind of see right but you know geographic area is not a box like this the world is not a box like this you might have roads and hills and mountains and ditches and things and But ultimately we can you know we can mount things in on a post and a you know things like that in an industrial area we have to think about like how that can withstand the weather damages also right people or animals right people so you have to make sure it's Out Of Reach so that way people don't go and grab your things and destroy it and and then also you know so there are like or birds attacking it or damaging it or other things so there's considerable environmental impact when you in in implement or install these things questions okay let's stop recording let's take a break
2024-11-12 20:13


