AI Recitation. How to Make (Almost) Anything (Almost) without Making Anything
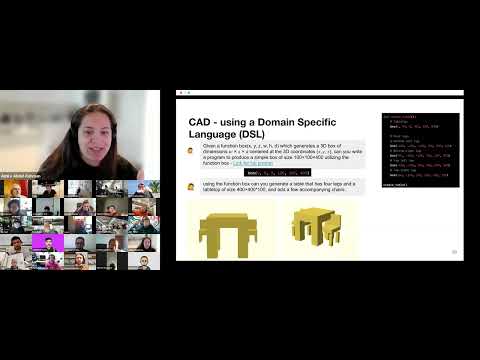
okay welcome to the AI recitation uh AI on one way to measure it has been progressing smoothly and continuously on another has been going through boom bus cycles and right now we're in a boom cycle this one is very dramatic it's disrupting almost everything uh including us and is pointing to a future where we may not need either students or teachers in the class since both can be obsoleted and so to talk about the opportunity challenges and threats we have a fabulous group so uh we're first going to start with a A group of grad students from MIT uh Val deir and Olivia uh then we'll go to Cesar and the Fab Network and then we'll go to uh one of the AI leads at zoom and as always these are interactive post um comments questions in the chat so uh Val take over all right well um hello everyone Let's uh let's get started so uh this lecture as Neil uh you know introduced is how to make almost anything almost without making anything implying that AI will uh hopefully assist us in the workloads um of making things so first of all um you've probably heard this many times before uh without AI you will you know be left behind if you don't learn it now you will be left behind if you don't learn it now you will be left behind this is a narrative that has exploded kind of recently but when people use the term AI what do they really mean uh this is something we will dive into here um for the most time they're talking about something called large language models um and large language models uh is something you might be familiar with if you've ever used things like chat GPT it's essentially uh a huge um model that have learned to predict the next words uh in a sequence of words and since it's been trained on all of the data on the Internet it's getting really good at predicting the next word um and this leads to some people using uh these in something called an agent where it not only predicts the next word you know if you give it a task like write an essay uh or write me some code but you can also connect it to what's called tools that allows it to um to decide you know something to use and then use it and then the things that it gets will be fit fed back into it and it can kind of uh use that information in a um close loop fashion to give an example um people have built you know systems like chat GPT but that have access to web search so it can search the internet then it gets the results of its internet search and then it can you know with that new information uh continue reconing about that um and produce new sequences of words um or for instance in the fabrication content you know you could have a uh large language model that is capable of you know sending a file to a 3D printer and then based on the result of the 3D printer it will sort of get that information back and can tell you how that went or the system can write code and then execute the code and then based on if the code is successful or or has a failure it gets the result and it can reason about this um this is kind of a new frontier and that's why we're sort of you know bringing this in uh as well because this might be something that you're excited about connecting to your fabrication uh um tasks that you're interested in so here's just a case of one of these agents thinking about something defining its own tasks then conducting a web search taking the results back and thinking about it more um and you can read more about this go if you read up on things like autog GPT um this is also something you can make very easily if you've ever tried the gpt's editor on on open AI uh in inside chat GPT you can you can do this very easily um and if you want a little bit more freedom you can use something that's called the open aai assistance API um it's also very well documented so just have a link to it here um and if you want full control you can use something called Lang chain um which helps you doing this too um and if you want to go completely open source uh and not use open AI there's this thing called mistol um uh this uh company so um another thing that's also extremely exciting is in your fabrication projects you can not only use language or words um you can also now use video so I'm going to give an example of someone who used a uh large language model in combination with images to uh create this kind of uh verif uh uh David adenor AI clone so it's essentially it takes an image and then this image is fed to the large language model and it returns text and then the text is is run through another model that changes the text to David Aden brough's voice and here's an example and now as I move around he here we have have a remarkable specimen of homo sapiens distinguished by his silver circular spectacles and a man of tousled curly locks he is wearing what appears to be a blue fabric covering which can only be assumed to be part of his mating display so as you can see you know you have on the top Corner the picture that it's looking at um and yeah um it's very fun and you know you can embed this into if you're building systems with cameras all of a sudden you can build systems that have extremely uh uh uh you know you know detailed insights into what's happening um and yeah I have a link to this also uh here at the bottom and I'm sure Neil will share the slides later so you can try it out it's very fun um all right so let's make each class almost obsolete um using generative AI so we'll go into three distinct categories computer cre design then we'll go into 3D modeling and then we'll um end with kind of electronics design and program gramming um all right so first I will pass this on to Amira hi everyone um so yeah so I was I'm going to talk today about like um using large language models for Cad and cam um so like basically in context of like the assignments that you uh guys are going to do throughout the year um if you go to next slide um I just wanted to um sorry can you do go to next slide yeah I just wanted to give like a disclaimer um like here we're talking about how to go from text to kind of to CAD or Cam like um and uh in in in general there's like a lot of research on on like how they how they train to go from text to um like given like large um data trained from text to cam or but like this is using Gans and Transformers but we're not gonna be talking about this we'll be basically talking about large language models and chat GPT in particular uh and and this works uh that the large language models goes from text to code um and this is kind of um because there's like um it's it's well trained to go from text to code and then manually we kind of use go from code to the cad like environment and this is using like either a create your own language um uh which is going to show or you can also use other apis like cat open source apis or other apis in Python um so you can go from the code to the cam manually in in a like separate uh process afterwards um so if you go to the next slide kind of um the first kind of experiments we we were working on was was like how to give in your own language so you give it for example here we asked J gbt to uh we tell it there's a function box that like gives you the center of the Box you give it the center of the box and the dimensions and you wanted to you wanted to see the spatial reasoning happening behind um chat GPT if you ask it to create um um like a simple box so here it created a simple box then if you go next if you just uh then um you can ask GPT using this like function that you just learned uh can you create a table that has four chairs and as you can see actually chat jpt was able to um to understand what this chair is and what is a table and that they're created of different boxes and it was able to generate the thing of course it only generates like the function on the right uh and and like I manually like use like kind of visualize what's happening uh just to see like if it's correct or not here the scale was not correct so I asked CH to um CH to fix the scale it was able to fix the scale but some other stuff like kind of doesn't work in the between so you can see that kind of it's more like an iterative process if you go again like I fix I told it to fix like kind of the thing so it's it's kind of it does work but there's like a lot of things that could go wrong and there's like still like there isn't like um because basically the large language models only understand like the text it doesn't like have any validation of what's happening there isn't like a spatial reading like kind of it doesn't know the C it just goes from it's a large language models that go from text to code so so there's like a lot of things to kind of but like once you have the code you can fix it but like it's not like an automated process that would happen like right away um if you go to the next slide this this one for example uh I asked you to create a simple cabinet using um open GS CAD this is like a um open sour like a card environment in JavaScript um and it's it was quite impressive that I was able to create the code with functions and hierarchy it learned like hierarchy it's parametric so you can later change the code of course I had to manually like fix some stuff like the code doesn't like sometimes the the it doesn't give you some of the uh dependencies so um but like again the the code was very well structured very um it was able to create like kind of uh variables and and parametric way and and different functions so you can added the code later to change so this could be a good starting point in the cad like um in your CL cting workflow um this one I thought was super interesting because um I this this is using py Vista which is a cad um um library in Python uh which um I asked jpt to create three bio inspired um um uh like kind of um fish so J GPT even though it doesn't have any like images like it doesn't have any spatial it created like a goldfish it was like even the Cutters The Chosen colors like it the code the whole code is kind of um like it was is able to know like what is a cfish how does it look that it's created from a sphere and like given the the kind of constraints of the language so um that was quite in interesting um and if you go next um finally like this is the new library that I found um I came across so um so this one um you can it's able so they created like an agent um trained using their own API I think it's like zoo. they have their own like coad so you can here you can like create like more CAD it's it's trained for the cad so it's like um and you can kind of write what you want and then download the right way so you don't have to do the extra step of like having your own like kind of thing uh of course like here you on like download an obj so you can't like actually edit later so it's not like I I prefer having a code that you can change later but like it actually works better because it's like trained only to do from text to cat so this is if one someone want to play with it um then going next to after you have a cat like how do you go from how do you use like CHT to do more like CNC or like kind of Machining or uh or more um cam um so um and then like here we were uh kind of the like in your laser cutting assignment um is basically ask it to create like a a geometric lamp that like kind of have um that is intricate enough but also um could create like kind of is from laser cut so this is what it created I I manually created like kind of the on the right like the I like got the pieces and put it to be laser cut but it was able to do it it wasn't from the first time but it was able to know like how do that pie pieces intersect and and kind of remove the intersection so you can also use it for creating like laser cutting assignment um if you want it automatically um to next U next slide um to create like kind of a cut piece so here like for example the this is the maximum complexity I was able to do for a CNC uh week um so asking it to like giving it the Wood stock like what is the sickness and and kind of wanted I I kind of pushed it to create like more intricate like joints but it wasn't able so this is kind of but it it basically created an SVG file that give you the cut file that you give to the CNC machine right away um and and it was able to understand like that there there's joints the like kind of the thickness um and and put like it could also label the things for you um and if you go to next slide um um and basically you can only also use the like the large language models not only to create like cut files but also to ask it for like what is the optimum manufacturing processes so if you give it like a code that describes the geometry and um and tell it like this is could should be made with for example with plastic or or kind of with um like different materials it would tell you for example yeah this should be done with the CNC machine or like the injection molden so you can ask it like kind of in brainstorming at the beginning or um this is like these two images from a paper that they go more like I I us should check this paper out but I kind of also you can give it um a text like a code for like for geometry and ask it like if I'm want a CNC machine this can you fix can you tell me what is the potential problem so chpt was actually um able to understand like the the there's like parts that has small radius or the wall thickness um so it it was able actually also to fix some of the stuff or like kind of to um to um show like there there's problems and and some of the designs um yeah um and finally this is this is more on like this like verification or simulation what if like you have a design but you want to verify that it works um um like until now like you can't like kind of ask it like the the maxim for example of the chair is it like strong enough or not um so on the left like here like if you ask it if um if this like chair is able to withhold like 100 kilograms it was able to give you like kind of an an analytical description didn't give like the it didn't show like where it got like the the real like formula so you have to trust it in the process but it was kind of able to reason that the chair there's like 100 kilograms where the forces are so you can use it in that direction or on the right if you want to do like FAA and like um so you can ask it to generate the code to do the FAA then you can like kind of interpret the the results um yeah finally I just wanted to then like last slide to to just like an as a summary um it has like still has like a lot of things but there's like a lot of limitation it's able to understand spatial reasoning a bit uh constraints there's iteration which is very good like you have to kind of fix some of the stuff which is good for debugging um as well as like for you're able to to have and it works very well with modularity and hierarchy so if you start with like um I I found it like easier to start like kind of giving it a function and start like building on it like first can you create a box can can create a table can you create two tables like going like it's it's it's it understands better if you do that the limitations of course like it it doesn't there's no validation it's not able to verify what's happening and also in the scalability like if you ask it too many stuff like then the constraints like it forgets what happens before um um and I believe like later like when there's like more um training specialist training with like CAD or like kind of because all we're using our large language models without like specialized like kind of libraries or like kind of um giving more like data this more C I think it's going to be get better but it's like it kind of works now um yeah that's a that's it for them cool so now let's uh dive a bit into uh the 3D scanning and 3D uh modeling part of the course so for those uh who are familiar with 3D modeling um not using a cat tool typically looks like this which is extremely tough um uh and time consuming but recently uh you know there's been new approaches for this so one is given images of things in the real world can we construct a 3D model and then the later more perhaps like newer way of doing it is well I will just type a text description of the object that I want and then I will use uh a generative AI model to build this thing for me um so you know if you're interested in the whole writing some text and then getting an object out of it um there's this whole like uh open source Studio where that has a bunch of models um that you can use uh um but there's also this uh company called Genie uh Luma AI that has the service called Genie where you can essentially in a matter of seconds and we're going to try this right now hopefully my the screen is shared um but um yeah let's try a monkey riding a sausage and then within seconds you will sort of get an output um oh here's a monkey riding a sausage so these are 3D objects that you can then download and you can 3D print it you know you can go back and change the prompt to something different um and yeah it's super useful but uh one of the limitations of these is that the quality as you might see um is not super good of these uh of these models um so let me go back here again okay cool so um okay so uh a project that actually started uh in uh in this class the MIT version with Neil was uh trying to build a uh model that can convert text into 3D uh in such a way that it has high detail and it can become something real um when it's 3D printed and these are the results um and here are some more results so this is a salt shaker in the shape of an axel um and this is a teapot made out of leaves uh using this and um yeah and it's available online if you want to try it um you know feel free to follow this link uh okay so one more thing is the electronics design typically when we design Electronics we first try to figure out you know what are the things that we need um then after we figure out what we want to do what we need then we build the schematics like which components uh how do I connect the different Electronics components um and the last thing is writing the the the the code itself that goes onto the the circuit board to enable all the functionality that I want um typically uh you know we have to read a lot of uh a lot of uh text in order to figure out what are like how to connect the different components what are the maximum temperatures and stuff like that uh and it can be quite overwhelming thankfully now you can chat using uh these large language models with these PDFs and uh expedite the process a little bit so here's an example where I'm taking a data sheet of an ESP 32 um and I'm simply just asking it you know what are the pin definitions of it um and then it's taking me to the page and I can even follow up with it and ask it where I can uh um in this case connect a temperature sensor and it will give me the pins that uh I might be able to use to do that so that's super useful um again you can also ask chat to help you figure out like which pens you can connect um uh and it can also write the code for you um but you know if if the llms can do all of these steps why don't we just bundle it all up together and so this is a project whoops so this is a project um where we put it all together so this is also open source and available we put it all together um and here you know you can just say something like I wanted monitor my Greenhouse and then it knows the components that you have and it can suggest something um so here it says you can use a humidity sensor which is what you have um to read the humidity levels would you like to proceed I say yes it tells me where to connect the different pins of the sensors to the AR arino Nano that I'm working with so then I just do that um and then when I'm done then I just okay I have connected the things um and then it writes the code for me and uh uploads the code to my board which is connected to the computer and then as you can see here I just simply put the sensor in there um and I read the result uh from the humidity sensor so super easy to use uh very fun um and works for simple uh designs all right right um I will skip this because we're a low on time but um feel free to look back at this um at a later section okay so I will pass it on to Olivia now thanks Bal so um I'll take over the screen share in the meantime I'll just share a bit about how last semester we took this version of Fab Academy um but at MIT to explore the question about whether or not an AI student can almost make things and ultimately I think as Val and Amir have also shared we kind of found out that while LMS make it easier to produce artifacts and write code it really only serves as a starting point for Learning and exploration we found that while it was sometimes inspiring I think human discernment and creativity and collaboration cannot yet be replaced uh but that's it we also saw the potential of AI for simulating AI Partners collaborators and teachers and and to this end this recent research from last year showed how AI can simulate how Pairs and groups of people can interact uh to a surprising extent of reality so uh while this research simulated a casual environment we together with our AI student tried to replicate this to build a Fab BLB environment let me show you welcome to the land of sorry I will show you how that looks like with sound here so this is a fabrication lab that is um open air open air Fab Lab I'm not sure if you can hear that but that's Neil's voice and so this is where we stored all of our week's assignments for the AI student um and you can come over here to this URL to check it out for our final project we created this website so the a open air fabrication lab um and our student AI Leen uh was the one who helped us to complete all the assignments um we asked Eileen for an final project idea and she proposed an indoor garden but we wanted to take it to the next level so with some of the AI student ta creativity we created together an aifb knowledge Garden instead together with aias and AI Neil otherwise known as nail um and if I can close this I'll show you what it looks like you can walk around and you can talk to the electronic spch for instance get some information on how to use it you can also approach a TA like AI instructor Leo here and ask um how do I make a laser cut lion for instance and Leo will function as your ta and give you some helpful response hopefully there you go so you can go back and forth just like you might on chat GPT but the difference here is that you can also talk to other students and collaborate that way um you can feel free to come to this website to explore it but it only works when the server is running otherwise you can check out how it works on this video as well so going back to my slides um we kind of wanted to touch a little bit on the limitations and ethics of using AI for fabrication um as you might have encountered AI doesn't always fully understand the context the human context and so this is something that we must always be conscious and wary of um there are a lot of politics and controversy involved with using Ai and this is definitely something that know policy and laws are currently being updated um so we need to keep an eye on that once again this is our conclusion from before and we're so excited to see what kind of things you can do with some AI ower creativity well thank you so much again from the three of us um feel free to ask any questions great thanks uh Val delivia Amira all grad students at MIT doing this work uh both both technically and yeah posing these really provocative questions when VA did the print something assignment by asking um tat gbt for a Serial teapot it wasn't clear did he do the assignment and who did the assignment um uh the these really interesting questions and challenges and we'll be posting all of their slides afterwards so there we're going to go on to Cesar who's representing a group in the Fab Lab Network that Loosely started picking up from valmir Olivia but has been looking more broadly at what are the implications of AI and how we do what we do so take over Cesar so yeah hi everyone I hope you can H see my screen so we're going to discuss about a group that launch at the at the instructor boot camp in Leon and we were figuring out okay this this project from B Olivia and Amir was really cool but how do we embed this into Fab Academy way of doing things so we created a group that so far is called Fab Academy aab H we plan to have bi-weekly meetings so when these ration are not happening we will be just meeting and keeping up with all the updates in the in the groups so far everyone engage is well was already on this trctor group but we think it could be open to everyone in the network so if anyone is interested um HK launched last week on MOS channel so there is this fa Academy AI Lab at MOS so if you are interested in what you're are going to see feel free to to join so what uh we have just a couple of meetings discussing what could be useful and we have so far talked about creating the a student that that has its own gitlab account and content we were also talking about customizing gpts and mapping the solutions for generative AI what what can be done so far and try to keep it updated over the years and even we thought about having Neil interviewing the students to figure out if he could answer properly answers about its own created website contents so could we call this the garon F touring test as a inspired by the by the other other touring test there's a lot to unpack on this line so I'd like to take a couple of minutes to explain about the custom IG GPT some of the challenges opportunities about the Cs and Nots and how does it apply to the to the AI world so but also the C GPT and also Amir try to customize um so the first question could be can we just take the fa Academy archive and put it onto a GPT it could be at the starting point like creating the documents and try to have a simple way to work with this but there is a limitation for the GPT for uh GPT so far so you can only fit up to 20 documents otherwise you need to unpack maybe one archive per year and then maybe it's grow bigger because the maximum size is like 52 megabytes so and some people have just realize that once you start putting tons of content into the gpts it starts to slow down so maybe you need to create one GPT per session or try to split the content in a way to make sense uh this could be like a good starting point to have like this kind of specialized assistant for each of the sessions where you can ask your laser instructor or your cut instructor to offer use on help based on all the previous knowledge of the available F Academy archive we were also shown some of these large language models like gp4 and right now there are tons of commercial of the self AIS like dpt4 Gemini Ultra that have been like released last week and you can get any of this but there is the alternative of commercial of theel with open weights and I think Walter will be very happy to know about the Lama model for the for from meta that is available of course as a service but there are also tons of Chinese model coming from alib Abad and even some models that help you coding better so we were also figuring out can we tune this model to help the student perform better when they're creating we were also discussing about the the one of the things that Olivia cover in the last part about the ethics that it could be like required for students in the same way that they they document what they do maybe they could share the proms if they use the gpts to document what they they're doing um one really good announcement two weeks ago H alen Institute it was like last Friday alen Institute released uh the first kind of real open source model where everything is available weights data code because there are tons of model that are offering you like the binary format just the the binary format but right now there are models where the whole recipe is is shared like the way it's the data so you can track if like copyrighted material was used to train the model or not and this could be could lead to a more ethical way to train all these H future models so in terms of what can be done usually we need to combine the following techniques one is retrieval ad Meed generation where we create the contents we put into the llm so it returns better knowledge or Cates and just trct the relevant parts of the knowledge for us but if we want for example to train these models to produce valid open scat code or or other kind of more complex shapes we need to H run also fine-tuning techniques where we are providing like tons of examples so we can embed the knowledge into the model itself so when we are thinking about training all these models and moving beyond the gpts we need to combine like creating the information but also figuring out what parts need to be inside the model like to to gather knowledge about maybe geometrical parts and that kind of stuff and what part needs to be taken from from the outside because it doesn't make sense inside of the model itself if you want to find out what models perform better there are like um right now all the models that perform better the top 10 are proprietary models but if you want to find out what open models can you use maybe for your practices there is this open llm leaderboard by hugging phas where you can find out in different Benchmark what are the best models so if you want to find what is the best model for logical reasoning or for getting truthful responses you can go there and you can find out what is the best and the download link is usually right there so this is the main source when we decide about that and also regarding the site and this is something that H we were also discussing how can we make um AI tools embedded into the process so the students can uh document better share information better so one of the models that uh is being used currently and it's quite impressive that it work is whisper so this is a model that performs spech to text conversion so you can just press a button and say hey I'm taking this this piece of carboot into the laser cutter my my speed is that speed this is the number of BS and it will just get it down written for you and for these people that are not native speaking you can also make it like you can record it in your own language and have the whisper model translated to English to to written English so it might be useful when you are trying to document and you're are in the in the Flow State like trying to make things forward to have this um it's really really useful and it also works for 100 languages so given that the fablab network is all around the world it will help people in all kind of bank or language to get this translated properly the simplest app I've tried so far is one called whisper writer you can run it 100% on your computer you don't need a very powerful computer but there are options for if you're using Mac or Linux all under the hood are using the same whisper model that works really really well and it get the punctuation right you get the commas and the dots that usually don't need to do that kind of much postprocessing and also if you want to try local llms to find out whether they are able to to create code python code open Scout code or any kind of board H there are several option I'm saying here what what are like the best multiplatform is gbt for all you can even drop PDF drop your own repo from gitlab it will answer questions based on your documents so that's really really useful you don't require any kind of GPU or something it just works out of the box but if you want to get a bit farther there are some other options like Studio or Lama and if you want to get down into customizing things there is this called Tech generation web UI where you can load any model on the internet and find out it's the thing that that works for you and yeah for those Spanish speaker I'm just trying to documented in the open in Spanish we will put all this information also in the in this mother mode Channel we will publish it on the git Cloud we will try to distill all this information so we can keep track of what going going on in the AI world with open source and also commercial models and that's it for me great uh thank you Cesar uh now I'm pleased uh uh in in the upper left of your screen you might see a pulsing star which is zoom's AI companion and I'm pleased we have chenang from Zoom to talk about um uh both I want to share with them our use of zoom and then talk about the uh Zoom activity so please take over yeah thanks d uh let me okay so uh thanks a lot I'm really honored to be here to talk about our Zoom AI companion strategy and uh so I'm changu I'm an AI science lead at Zoom so first uh quick uh introduction of the zoom company itself the the full name of Zoom is uh Zoom video communication it was founded about 13 years ago and from the first day it aimed at like removing the barrier of physical distance in real-time communication and as of today hundreds of millions of people including you have been active users of Zoom so while uh many of us have been using Zoom meetings we actually provide a suite of efficient tools Beyond meetings including but not limited to chats males and recently document processing and we also support various business applications such as contact senders sales and more one question people often ask is being a video Communication Company why do we need AI actually the short answer is absolutely yes because if we uh take a step back and look at all the business scenarios we uh serve such as meetings chats and documents they lie at the the center of decision- making process of people think about when business Executives want to reach a decision when teachers and students discuss something important and want to uh like have some brainstorming these are the high level human intelligence activities so if we can use AI to boost to help this uh this process to facilitate this uh thinking reasoning decision- making uh for humans it will be very very useful so by engineering alone what we have already achieved is definitely we have the we have digitized the whole process right we have this amazing software to make sure the communication uh is smooth but only by AI can provide the core assistance to facilitate this uh functions and a few years ago this task had been uh done difficult but since the Advent of llm we have found a way to adapt this llm to zoom scenarios and to help uh U support the scenarios that's why we have pushed forward the zoom AI companion feature which is uh this uh Star as an has mentioned uh it was available back in September 2023 in the first such AI product in uh communication software and a big advantage of us uh over other competitors such as uh teams copilot is that we have no additional uh pricing price tag for all the paid Zoom user accounts so if you already already have is a are a paid Zoom user you can uh get this feature for free so let's take a quick tool of what the zoom AI companion can support right now uh first is AI companion questions where you can uh ask questions any questions in natural language format during a meeting to the stop to this assistant and for instance if you are late to a meeting I often do that you can let it do Qui catch me up so you can summarize the meeting up to now like before you have joined or you can ask it like who uh what had Chang or what had um nail said like while um I was away things like that and after the meeting it can provide a succinct uh summary to the meeting this is particularly useful when you have missed a meeting but you want to get quickly get the gist of the meeting including the next steps with uh the person to execute the action time the item Etc and and similarly we provide summary to uh chat histories for instance you while you away there has been a long list of reply to your uh message you don't have time to read all of these so you can let it summarize it for you and then even have it to compose or polish message for you so this is an example of uh composing messages in email right if if you want to have a draft and also if you want to make the current draft longer or more humorous Etc it can help you with that so with that said I want to talk about the core technology behind this amazing AI companion feature if we take a step back and look at how traditionally tech companies choose what models to serve we found that most of the time we choose we like uh curated a lot of model candidates and then tested them on the validation data and then we choose the model with the best performance on the validation data but this is actually the best average performance for instance it could be the best accuracy on validation data or the highest human score on validation data right and we serve this single model candidate we sometimes have AB test but again the goal is to serve with only one model instance for any user input but what if we can choose smartly choose the best model for every input instance by some Oracle right for every different users input we can smartly choose the best model among our uh Arenal of models at least approximately so if actually with found that even for models uh as strong as gbd4 it doesn't have a monopoly over all the space of user in input instance there are cases where each different model in our suite that can like achieve the best output for a single user input instance but to do this it's easier said than done because there are two obstacles first if we really want to choose the best model output out of all the models we have naively we need to run every model once for each input then that's two time consuming and also the cost will be super high secondly and I think it's more difficult is that we don't know the quality before the user gives feedback so a naive way would be to show every models output to the user get their feedback and then show the out output with the best feedback to the m definitely this is not feasible so we have a device in approximate way that works pretty well in real scenarios we call this a Federated AI as described in the next picture so this is the core technology we uh in it uh we have two Central Concepts first is what we call model chain instead of serving only one model we serve a sequence of models model one model two and Etc usually these models are sorted based on the an increasing performance but also at an increas in cost so model one may cost like maybe the least costly model uh the performance is relatively weaker compared with other models and model 2 is a bit more expensive but more powerful or the quality is high and the second uh concept is called Zora this is surrogate quality evaluator that can give a numerical score of how good it thinks the output is based on the input output pair right now when the input comes we first serve it with model one the cheapest model and it comes with an output traditionally this output is directly shown to the user but now instead of doing that we first fed it into the zcore which comes out with the score We compare it with a predefined threshold D1 and if it's above T1 means it's confident that this output could be showed to the user because the quality is good then will directly show it and end the process only when the score is below the threshold do we send to the next more expensive and poal a better model and then similarly the process goes on the core idea of why this uh whole process works is that because of the long tail uh we found U we found that uh most of the questions are relatively easy like say catch me up or what other action items so here most of the traffic so here's an example like 90% of traffic is only processed by one model only or plus a very relatively much cheaper score and then only a fraction small fraction of traffic needs to be dealt with by more than one models therefore the amortized cost is low while the performance is is high because we have this quality assurer right uh where we only output to the user when we are confident and in the progress we train the models and zorer just like the way they're being used in inference during our training so each model is already accustom to seeing the feedback from previous models in the chain and also the input also the scorer is trained to be able to judge with high quality to align with human scores Let's uh quickly uh take a look at the the results so here I'm showing the comp comparison between our Federate AI solution with uh versus gbd4 as a surrogate for co-pilot I will compare in two Dimensions cost as serving cost to us and quality in two scenarios meeting queries or meeting questions and meeting minutes so we compute the cost based on the real numbers we have in our serving clusters and also our uh API cost or or in other words the am amount of money we need to pay to uh open AI for our usage of the RPI of gbd4 as you can see our cost is very small fraction of uh gbd4 which is only a 6% while the quality which is being judged by gb4 itself because the output of me both meting quy and meeting minutes are uh in natural language so we use you before to judge uh there has been literature showing that gbd4 or any model llm has a bias to label their own models output with higher quality score so even with that bias taking into account we still achieve 99% and 97% of the quality score of gbd4 so this shows that we have achieved our previously uh set North Star which is like low cost and high quality and so the to wrap up so uh in this talk I show the zoom AI company I highly encourage uh anyone uh who hasn't tried this uh to have a shot uh and uh also the core technology behind it okay thank you very much great thank you so much um to show the thoughtful back end and you should all know this is part of a a great conversation with zoom where we're giving them feedback on our use of it and for them this is a large Global multilingual multi everything um meeting that's a good test case so uh this is part of an ongoing uh collaboration with zoom so let me now so if you can stop your share um a couple notes a few uh final projects and then a little bit of time for Q&A so first um in the agreement students sign we ask them to credit sources and that includes uh AI engines and that includes prompts so just to note that the role of using AI in the class is clear you're welcome to use it but need to identify it uh one caution a few people have mentioned I want to stress is things like the electronic example of knowing which pin to connect to it's wonderful and powerful and often wrong or sometimes wrong so you need to be very cautious about um a hallucination generalization you can get an answer and a lot of the times it's right and sometimes it's wrong and so you really need to vet the engineering answers another comment is this session is focused on llms but also a lot of the impact doesn't involve launch language models it also just involves optimization so for example uh my student Jake has a paper coming out on a 3D printer that does instrumented to do rology so it can learn how to print recycled and renewable materials and that's really about search and optimization against uh richer data um uh one more note this recitation has largely been about things happening in the cloud in the embedded programming week I pointed to all of the progress in embedded Ai and so the something like chat GPT uses a hideous amount of energy and GPU resources there's been a lot of work to simplify them including what chenang presented but or in addition there's a lot of work to boil all the way down to things that work on microcontrollers seed has been very active on that and so through the cycle we'll be seeing more and more of embedded AI um now I want to come to I'm going to share an image on Fab Futures so after the Fab event in uh bhon we were asked if we could help with vocational training and what I proposed is there was a lot of and this is to many parts of the world you know 20th or 19th century vocational training rather than 21st century vocational skills and so I proposed using fablabs academi to teach 21st century vocational skills and I gave them a menu of possible topics like these examples on the slid from Jean Michelle who's helping coordinate this and we offered them these as things we could develop and the response we got is we want all of them not any one of them and so what that turned into is a class we're developing we hope to start in the fall called Fab Futures and it's a very different model Fab Academy is a deep dive with a cohort Fab Futures will be one month Hands-On introductions so in AI in a month you can train and use a model in Big Data you can analyze a DAT data set um in cyber security you can probe and breach of vulnerability in robotics you can um uh program a robot in microelectronics you can make the transistor these are one month units taught by global leaders to work groups like a Fab Academy and it never stops and it never ends it's a continuous uh rolling uh one month cycle um that goes forever and you can come in and join whenever you want and go off and among these classes the ones that really get traction um will spin off into deeper dive classes so this will be one followup in Ai and a number of neighboring things um this was inspired by Bhutan but we expect many sites all around the world are going to um participate the you know the the roughly 100 sites in the Fab Academy and the thousands of Fab labs and what's particularly exciting about that is Fab Labs up until recently were defined by the laser cutter by the tools but as it grows from fab Academy to fabri Academy to bio Academy to Fab Allin and now Fab Futures it's really coming to be defined not by the tools but by the culture and the community that we're assembling it's a really interesting moment in the life of the network so with that we have just a few minutes for questions and I want to start um uh so question about future about the cost the way that's going to work like all of our classes is all of the digital content is freely available the cost is for things that consume resources so real-time participation with the global experts and um accreditation and evaluation backend infrastructure things participation that consumes resources will cost and the pricing is likely to vary based on the cost of the units based on what each unit costs the content will freely share as we do with everything that has a little incremental cost um let me start with a question to Jean Michelle which is in this Fab Academy cycle we had started talking about some AI students and an AI lab like um the team at MIT did but you had some broader thoughts of what we might do can you talk about that yeah I I thought says I would also talk about it but we we we spoke in the in the a i group about the idea of instead signing up instead of signing up a student to the Fab Academy basically making a an llm for each week uh and so you you create an AI that has um sort of hyper expertise on on one week subject and then you can go as a student to these large language models and ask it questions and then eventually we could even imagine a a sort of a group session where we invite all these llms as Specialists and talk through the Fab Academy as a whole where these llms basically have their own um specific knowledge um and that would then eventually lead to you know what what you said Neil is like could you at some point obsolete yourself and then all the students as well uh and and there were other things we spoke about I'm not entirely sure what they were anymore I was I was focused on something else Cesar do you remember other other ideas that we wanted to develop instead of just just signing up a student we were also talking about this idea of connecting mods to the real world like can we connect the outputs of the llm to the mods so we can ask a pron get that intermediary result we can verify and then this could be shipped to the actual machine and then we had the concerns about what if there's an hallucination or if the code is wrong so we were also talking about maybe we need to have some digital twins inside mod of the laser cutter so we can send the information to the virtual serial print and find out if the machine would return an error or not but maybe for machines it's more complex but we were also discussing about getting this virtual Shia board where we can send the code to the board and it can be run and we could like test if the code is right or test if there is any kind of compilation error or things like that trying to mix the physical and the virtual very interesting that touches on a couple related things just I'm showing um for chenang this is mods something I initially wrote a whole um team's TR intoo Community project aimed at turning any format into anything to make on any machine and so I love the idea of AI Cloud connected to this now um a few years ago my lab was part of a uh research program to implement morphogenesis as a design principle so search over developmental programs and we were very constrained by the simulation engines for the digital twin searching over the physics the simulation engine kept breaking and so we've done a lot of work on multiphysics modeling um um and I'll be posting a paper shortly on that on connecting physics and modeling um this I'm showing this is a class I teach uh this is a Cambridge press text and these are notes for it on mathematical modeling and search and optimization and so that's I think that's going to be a growing part of the simulation Tools around the fabrication tools and this also touches on Ricardo is asking a question in the chat about sheet metal forming robots analy measuring feedback and he's asking what kind of AI they're using and again this is where I would distinguish um AI is being misused to mean many different things you broadly I would connect it to cognition and language um in a class like this I cover search and optimization which is beyond what I can do in faab Academy um it is part of um right now I'm doing the um my occasional machine building class where we we'll be doing um some discussion of that but this would be a great Fab futurist topic search and optimization is given constraints and given observations how you make something extremal and there's a whole family of techniques for search and optimization that get used against language for large language models but you can use in many other domains and I wouldn't even really call that AI it's just searching optimization and that's a very powerful technique growing so instead of you knowing speeds and feeds and knowing how to do path planning the tools can learn how to do that by by searching and optimizing so we're up to 10 o'clock any final questions or thoughts um let's see can AI create a stone it cannot lift my version of that is in the last instructor meeting you know we had talked about Mak uh the virtual students and I'd say the MIT students in the the AI students would have gotten about a B minus you know they might have passed the class but not with a great grade we'll see if they get better but then in the last instructor meeting there was the observation we could make the AI Neil so turn me into you know I'm I'm very predictable in all sorts of ways and turn me into an engine but then that leads to the AI students could be talking to the AI Neil and then what's left we all go off to the beach so um provocative questions uh it's not time to abandon learning all the things we learn because the AI systems make mistakes but it is nibbling away at a lot of the skills we teach and really transforming them so with that I'd like to thank everybody who presented um remarkable unfolding story I'll collect their slides we'll post the video and themes from this uh will be thread throughout the Fab Academy cycle into Fab Futures and Beyond so thank you all
2024-02-20 03:47


